广告系统中的在线策略引擎设计
在广告投放平台(ADX)的核心链路中,**流量精细化管控**是保障广告请求稳定性、提升资源利用率的关键环节。本文将围绕 ADX 系统中 <font color=tomato size=4.5>adx-smart-strategy </font>模块的设计思路展开,结合新增的「SDK/API 流量混合控制策略」,详解基于策略模式的广告流量动态管控方案。
一、背景与模块架构
1.1 业务诉求
ADX 系统需要对广告请求做多维度的在线管控:
- QPS 限制:防止单渠道请求量过高压垮服务;
- 扣减比例调整:动态调整广告消耗扣减的比例;
- SDK/API 流量混合控制:均衡 SDK(自有流量)和 API(第三方流量)的请求占比,避免单一流量类型过度占用资源。
1.2 策略特征
- 在线强实时性:必须在请求链路内快速决策
- 策略多、演进快:不同业务线、不同媒体位有差异化策略
- 数据依赖离线计算:策略参数通常来自历史统计结果
- 高可用要求:策略系统异常不能影响主链路
为此,我们将策略体系拆分为多个职责清晰的模块。
二、整体模块划分

2.1 各模块职责
**核心设计原则:离线负责“算”,在线负责“判”**adx-api(在线请求层)
- 负责广告请求的整体处理流程
- 通过 策略引擎 调用策略,不感知具体实现
- 只关心:是否命中、是否拒绝
adx-smart-strategy(在线策略层)
- 提供统一的策略执行框架
- 管理所有在线策略(QPS、流量混合等)
- 从 Redis 拉取策略数据,构建本地限流器
- 对外提供 StrategyEngine 统一入口
adx-smart(离线计算层)
- 定时任务统计历史数据
- 计算策略所需参数(如 QPS 配额、比例)
- 将结果写入 Redis
adx-smart-model(模型层)
- 存放公共实体、枚举、上下文对象
- 被 <font color=tomato size=4.5>
adx-smart</font> 与 <font color=tomato size=4.5>adx-smart-strategy</font> 共同依赖
三、设计目标
<font color=tomato size=4.5>adx-smart-strategy </font> 的核心设计目标:
- 可扩展:新增策略无需修改原有逻辑,符合开闭原则;
- 高性能:策略数据缓存到本地,避免每次请求查询 Redis,降低延迟;
- 低耦合:离线计算与在线执行解耦,仅通过 Redis 做数据交互;
- 易维护:统一的策略执行入口,标准化的策略实现规范。
- 安全降级:策略异常不阻断主流程
四、核心设计思想
<font color=tomato size=4.5>adx-smart-strategy </font> 的核心骨架基于策略模式构建,将「策略定义、策略实现、策略执行」分层解耦:
4.1 策略接口
定义所有策略的通用行为,是策略模式的核心抽象:
public interface SmartStrategy<T> {
// 策略类型(枚举)
StrategyType type();
// 执行策略(入参:上下文;出参:策略结果)
StrategyResult<T> execute(StrategyContext context);
// 策略是否启用
default boolean enabled() {
return true;
}
// 刷新本地缓存(从Redis拉取最新策略参数)
void refreshCache();
}
4.2 抽象模板类
封装策略执行的通用流程(模板方法模式),避免重复代码:
public abstract class AbstractSmartStrategy<T> implements SmartStrategy<T> {
@Override
public final StrategyResult<T> execute(StrategyContext context) {
// 1. 通用匹配校验(子类实现具体匹配逻辑)
if (!match(context)) {
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
// 2. 执行具体策略逻辑(子类实现)
return doExecute(context);
}
// 子类实现:当前上下文是否匹配该策略
protected abstract boolean match(StrategyContext context);
// 子类实现:具体的策略执行逻辑
protected abstract StrategyResult<T> doExecute(StrategyContext context);
}
4.3 具体策略实现
新增的「SDK/API 流量混合控制策略」是典型实现,核心逻辑:
- 匹配逻辑:校验上下文是否包含流量类型、SlotID 等核心参数;
- 执行逻辑:根据流量类型 + DspSlotKey 查找本地概率限流器,判断是否限流;
- 缓存刷新:定时从 Redis 拉取最新的流量配比,更新本地限流器缓存。
@Component
public class TrafficMixControlStrategy extends AbstractSmartStrategy<LimitResult> {
@Autowired
private PassSlotCacheManager passSlotCacheManager;
private final AtomicReference<Map<TrafficTypeEnum, Map<DspSlotKey, ProbabilityLimiter>>> limiterCacheRef = new AtomicReference<>(Collections.emptyMap());
@Override
protected boolean match(StrategyContext context) {
return context.getTrafficType() != null
&& context.getMediaSlotId() != null
&& context.getDspSlotId() != null
&& context.getDspSlotCode() != null;
}
@Override
protected StrategyResult<LimitResult> doExecute(StrategyContext context) {
Map<DspSlotKey, ProbabilityLimiter> typeMap = limiterCacheRef.get().get(context.getTrafficType());
if (typeMap == null) {
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
DspSlotKey key = DspSlotKey.of(context.getDspSlotCode(), context.getDspSlotId());
ProbabilityLimiter limiter = typeMap.get(key);
if (limiter == null) {
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
boolean pass = limiter.tryAcquire();
return StrategyResult.hit(new LimitResult(!pass, null));
}
@Override
public void refreshCache() {
String sdkJson = passSlotCacheManager.getMixControlSlot(StrategyConstants.SDK_TYPE);
String apiJson = passSlotCacheManager.getMixControlSlot(StrategyConstants.API_TYPE);
Map<TrafficTypeEnum, Map<DspSlotKey, ProbabilityLimiter>> res = new HashMap<>();
Map<DspSlotKey, ProbabilityLimiter> sdkLimiterMap = buildLimiterMap(sdkJson);
if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(sdkLimiterMap)) {
res.put(TrafficTypeEnum.SDK, sdkLimiterMap);
}
Map<DspSlotKey, ProbabilityLimiter> apiLimiterMap = buildLimiterMap(apiJson);
if (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(apiLimiterMap)) {
res.put(TrafficTypeEnum.API, apiLimiterMap);
}
limiterCacheRef.set(res);
}
@Override
public StrategyType type() {
return StrategyType.TRAFFIC_MIX_CONTROL;
}
}
4.4 策略注册中心
特点:
- Spring 自动装配
- 新增策略无需改注册逻辑
@Component
public class StrategyRegistry {
private final Map<StrategyType, SmartStrategy<?>> strategyMap;
@Autowired
public StrategyRegistry(List<SmartStrategy<?>> strategies) {
this.strategyMap = strategies.stream()
.filter(SmartStrategy::enable)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(SmartStrategy::type, s -> s));
}
public SmartStrategy<?> get(StrategyType type) {
return strategyMap.get(type);
}
}
4.5 策略执行引擎
封装策略查找、执行、结果转换的通用逻辑,为 <font color=tomato size=4.5>adx-api</font> 提供统一调用入口:
- 校验策略结果类型是否匹配;
- 从注册器中获取启用的策略;
- 安全执行策略(捕获异常,避免策略执行失败影响主流程);
- 类型转换并返回结果。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SmartStrategyEngineImpl implements SmartStrategyEngine {
@Autowired
private StrategyRegistry registry;
@Override
public <T> StrategyResult<T> execute(StrategyType strategyType, StrategyContext context, Class<T> resultType) {
// 1.校验策略结果类型是否匹配
if (!validateResultType(strategyType, resultType)) {
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
// 2.从注册器中获取启用的策略
SmartStrategy<?> strategy = getExecutableStrategy(strategyType);
if (strategy == null) {
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
// 3.安全执行策略
StrategyResult<?> rawResult = executeStrategySafely(strategy, context);
if (!rawResult.isHit()) {
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
// 4.类型转换并返回结果
return castResult(strategyType, rawResult, resultType);
}
private boolean validateResultType(StrategyType strategyType, Class<?> resultType) {
Class<?> declaredType = strategyType.getResultType();
if (!declaredType.equals(resultType)) {
log.error("strategy resultType mismatch, type={}, declared={}, required={}",
strategyType, declaredType.getName(), resultType.getName());
return false;
}
return true;
}
private SmartStrategy<?> getExecutableStrategy(StrategyType strategyType) {
SmartStrategy<?> strategy = registry.get(strategyType);
if (strategy == null) {
log.debug("strategy not found, type={}", strategyType);
return null;
}
if (!strategy.enable()) {
log.debug("strategy disabled, type={}", strategyType);
return null;
}
return strategy;
}
private StrategyResult<?> executeStrategySafely(SmartStrategy<?> strategy, StrategyContext context) {
try {
return strategy.execute(context);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("strategy execute error, strategy={}", strategy, e);
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
}
private <T> StrategyResult<T> castResult(StrategyType strategyType, StrategyResult<?> rawResult, Class<T> resultType) {
Object data = rawResult.getData().orElse(null);
if (data == null) {
log.debug("strategy hit but data is null, type={}", strategyType);
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
if (!resultType.isInstance(data)) {
log.error("strategy result type mismatch, type={}, expect={}, actual={}",
strategyType,
resultType.getName(),
data.getClass().getName());
return StrategyResult.miss();
}
return StrategyResult.hit(resultType.cast(data));
}
}
4.6 缓存刷新机制
为保证策略参数的实时性,同时避免在线请求直接查询 Redis,设计「定时刷新 + 本地缓存」机制:
定时任务:LocalDataSyncTask
通过 <font size=4.5 color=orange>ScheduledExecutorService</font> 启动固定频率(默认 60s)的定时任务,遍历所有策略并调用 <font size=4.5 color=orange>refreshCache()</font>:
public class LocalDataSyncTask {
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
private static final int SYNC_INTERVAL = 60;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
registry.getAll().forEach((key, value) -> {
try {
value.refreshCache(); // 触发策略缓存刷新
} catch (Exception e) {
// 异常日志
}
});
}, SYNC_INTERVAL, SYNC_INTERVAL, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
线程安全的缓存存储
使用 <font size=4.5 color=orange>AtomicReference</font> 存储本地缓存(如流量混合策略的限流器映射),保证无锁化更新的线程安全:
// TrafficMixControlStrategy中缓存限流器
private final AtomicReference<Map<TrafficTypeEnum, Map<DspSlotKey, ProbabilityLimiter>>> limiterCacheRef =
new AtomicReference<>(Collections.emptyMap());
@Override
public void refreshCache() {
// 从Redis拉取最新流量配比 → 构建限流器映射 → 原子更新缓存
Map<TrafficTypeEnum, Map<DspSlotKey, ProbabilityLimiter>> newCache = buildNewCache();
limiterCacheRef.set(newCache);
}
4.7 限流器设计
针对流量混合控制场景,实现「概率限流器」( <font size=4.5 color=orange>ProbabilityLimiter</font> ),核心逻辑:
- 基于 <font size=4.5 color=orange>
ThreadLocalRandom</font> 生成线程安全的随机数; - 通过率( <font size=4.5 color=orange>
passRate</font> )通过 <font size=4.5 color=orange>volatile</font> 修饰,保证多线程可见性; - 校验通过率范围(0~1),非法值默认设为 1.0(不限流)。
public interface RequestLimiter {
boolean tryAcquire();
}
public class ProbabilityLimiter implements RequestLimiter {
private volatile double passRate;
@Override
public boolean tryAcquire() {
// 随机数小于通过率则放行
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() < passRate;
}
}
五、核心类结构与类图
5.1 核心类说明
| 类 / 接口 | 核心职责 |
|---|---|
<font size=4.5 color=orange>SmartStrategy<T></font> |
策略顶层接口,定义策略类型、执行、缓存刷新等行为 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>AbstractSmartStrategy<T></font> |
策略抽象模板类,封装通用执行流程 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>TrafficMixControlStrategy</font> |
流量混合控制策略具体实现 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>SmartStrategyEngine</font> |
策略执行引擎接口,统一调用入口 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>SmartStrategyEngineImpl</font> |
策略引擎实现,封装策略查找、执行、结果转换 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>StrategyRegistry</font> |
策略注册器,管理所有策略实例(基于 StrategyType 映射) |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>LocalDataSyncTask</font> |
缓存刷新定时任务,触发所有策略的 refreshCache |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>RequestLimiter</font> |
限流器顶层接口,定义 tryAcquire 方法 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>ProbabilityLimiter</font> |
概率限流器实现,基于随机数控制流量通过率 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>StrategyContext</font> |
策略执行上下文,封装媒体 SlotID、流量类型等参数 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>StrategyResult<T></font> |
策略结果封装,包含是否命中、结果数据 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>LimitResult</font> |
限流结果封装,包含是否拒绝、拒绝原因 |
<font size=4.5 color=orange>StrategyType</font> |
策略类型枚举(TRAFFIC_MIX_CONTROL/QPS_LIMIT 等) |
5.2 类图(Mermaid)
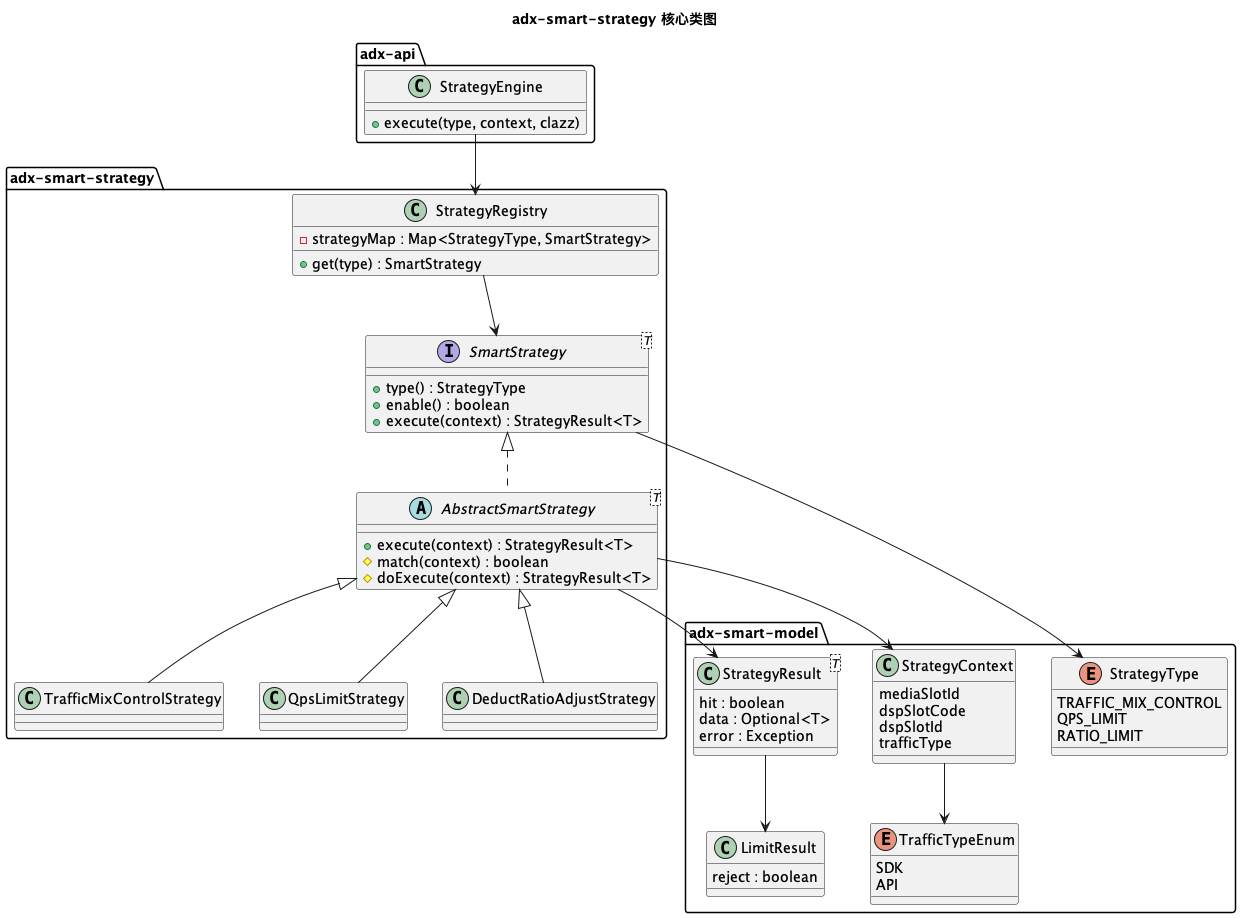
六、SDK / API 流量混合控制策略
6.1 adx-api 调用示例
private boolean allowByTrafficMix(AdRefDto adRefDto, ApiContext apiContext) {
try {
String mediaSlotId = apiContext.getChannelSlotDto().getSlotId();
// 1. 构建策略上下文(流量类型、SlotID等核心参数)
StrategyContext context = StrategyContext.builder()
.mediaSlotId(mediaSlotId)
.dspSlotCode(adRefDto.getPartnerCode())
.dspSlotId(adRefDto.getSlotId())
.trafficType(apiContext.isSelf() ? TrafficTypeEnum.SDK : TrafficTypeEnum.API)
.build();
// 2. 调用策略引擎执行「流量混合控制」策略
StrategyResult<LimitResult> result = strategyEngine.execute(
StrategyType.TRAFFIC_MIX_CONTROL, context, LimitResult.class
);
// 3. 处理策略结果:若命中且拒绝,则返回false(限流)
if (result != null && result.isHit() && result.getData().map(LimitResult::isReject).orElse(false)) {
apiContext.setApiReturnCode(ApiReturnCode.TRAFFIC_MIX_CONTROL_SDK_API_LIMIT);
return false;
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("trafficMixControl error", e);
// 异常时默认放行,避免策略异常影响主流程
return true;
}
}
6.2 策略执行流程
- 匹配校验:<font size=4.5 color=orange>
TrafficMixControlStrategy.match()</font>校验上下文是否包含流量类型、SlotID 等核心参数; - 查找限流器:从本地缓存中根据「流量类型 + DspSlotKey」查找概率限流器;
- 限流判断:调用 <font size=4.5 color=orange>
ProbabilityLimiter.tryAcquire()</font> 判断是否放行; - 返回结果:封装 <font size=4.5 color=orange>
LimitResult</font>(reject=true 表示限流),通过 <font size=4.5 color=orange>StrategyResult.hit()</font>返回。
七、扩展新策略的标准流程
7.1 新增策略
只需实现 <font size=4.5 color=orange>AbstractSmartStrategy<T></font>,实现以下方法即可:
- <font size=4.5 color=orange>
match()</font>:定义策略匹配条件; - <font size=4.5 color=orange>
doExecute()</font>:实现具体策略逻辑; - <font size=4.5 color=orange>
refreshCache()</font>:实现缓存刷新逻辑; - <font size=4.5 color=orange>
type()</font>:指定策略类型(新增 <font size=4.5 color=orange>StrategyType</font> 枚举值)。
7.2 新增限流器
实现 <font size=4.5 color=orange>RequestLimiter</font> 接口,扩展不同限流算法(如令牌桶、漏桶、固定窗口 QPS 限流器),替换 <font size=4.5 color=orange>ProbabilityLimiter</font> 即可。
八、总结与展望
8.1 模块划分
通过将策略体系拆分为:
- 离线计算(adx-smart)
- 在线决策(adx-smart-strategy)
- 统一模型(adx-smart-model)
8.2 设计优势
并结合 策略模式 + 模板方法 + 注册中心 的设计
- 可扩展性:策略模式 + 接口抽象,新增策略 / 限流器无需修改原有逻辑;
- 高性能:本地缓存 + 定时刷新,避免在线请求依赖外部存储,降低延迟;
- 高可用:策略执行异常捕获、限流器参数合法性校验,保证主流程稳定;
- 低耦合:离线计算与在线执行解耦,便于独立迭代。
8.3 未来规划
- 接入动态配置中心,支持策略参数实时调整(无需等待定时刷新);
- 完善监控体系,统计各策略的命中次数、限流次数、缓存刷新成功率;
- 扩展更多策略类型(如地域限流、设备类型限流);
- 优化限流器算法,支持更精细化的流量管控(如基于滑动窗口的 QPS 限制)。
<font color=tomato size=4.5>adx-smart-strategy </font>通过策略模式构建了灵活、高性能的广告流量管控框架,既满足了当前 SDK/API 流量混合控制、QPS 限制等诉求,也为后续策略扩展提供了标准化的实现路径,是 Adx 系统流量治理的核心基石。
