广告检索
倒排索引是搜索引擎的关键技术,而广告的检索上也采用这样的框架。但是广告的检索问题也有一些自身的特点和需求,基本的倒排索引技术在广告检索中遇到了两个新问题。
- 广告的定向条件组 ,可以看成是一个由与或关系连接的布尔表达式,这样的文档显然与搜索引擎面对的 Bow 文档不太一样,这里存在着有针对性的检索性能优化空间。
- 在上下文关键词或用户标签比较丰富,广告检索中查询可能相当长,甚至会由上百个关键词组成,这种情况下的检索也与搜索引擎中主要由 1 ~ 4 个关键词组成的查询有很大区别。试想,如果将 100 个关键词同时输入到搜索框中,返回的结果会是你想要的吗?
布尔表达式的检索
广告检索与普通搜索引擎检索的第一不同是布尔表达式的检索问题。
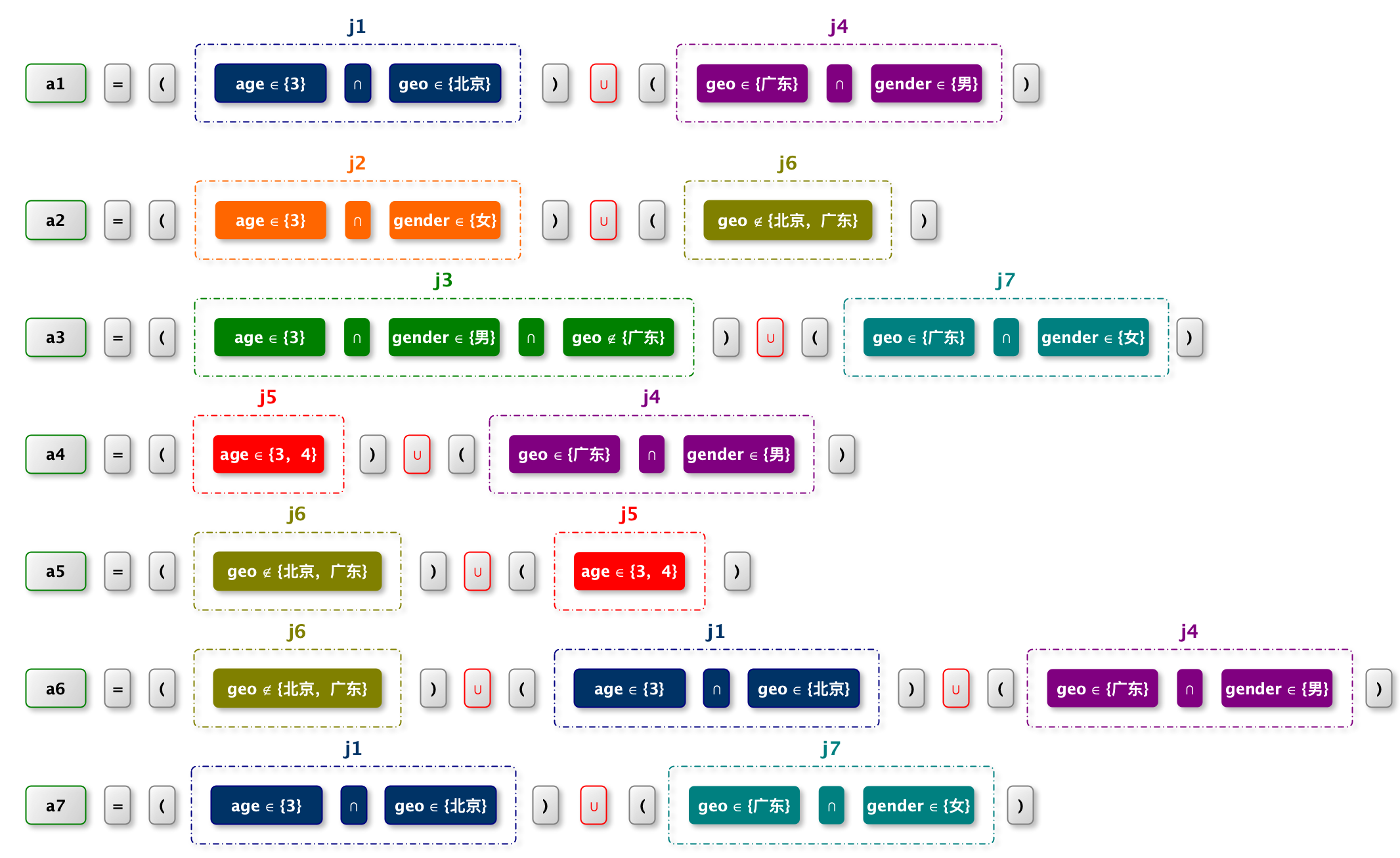
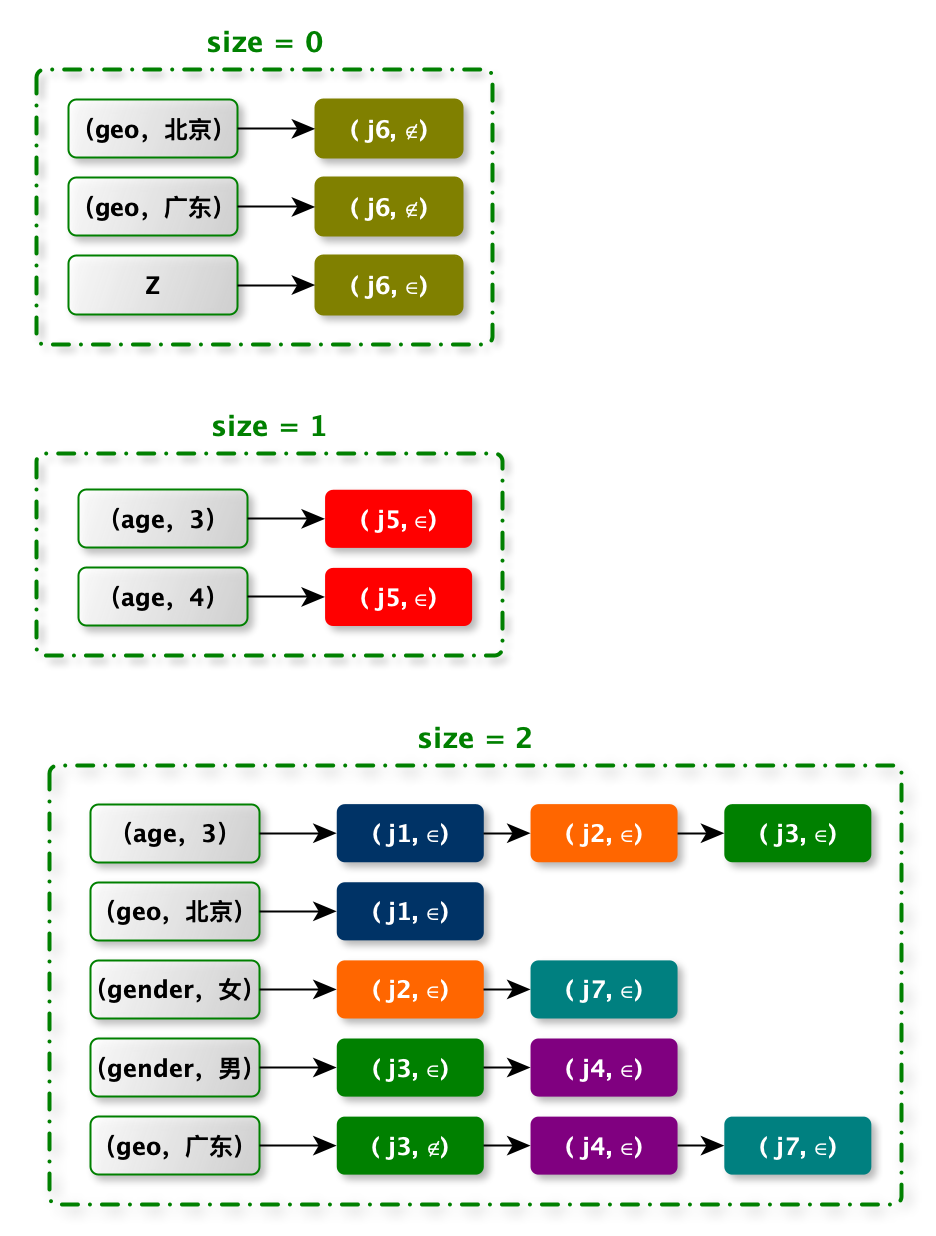
如下图:有 7 条广告的定向条件。
注意:我需要将定向条件写成析取范式(Disjunctive Normal Form,DNF)的形式。
DNF 中有两个概念:
- 每个 DNF 都可以分解为一个或者多个交接(conjunction)的`并`
- 每个交集又可以进一步分解为一个或多个赋值集(assignment)的`交`
布尔表达式检索的问题有两个特点
- 当某次广告请求的定向标签满足某个 Conjunction 时,那么 Conjunction 包含的所有广告一定符合当前请求。
- 因此需要对 Conjunction 建立倒排索引,并加一层 Conjunction –> AD 的倒排索引辅助检索。
- Conjunction 建立倒排索引
- Conjunction --> AD 的倒排索
- 因此需要对 Conjunction 建立倒排索引,并加一层 Conjunction –> AD 的倒排索引辅助检索。
- 在 Conjunction 的倒排索引中,有一项直接可以帮助我们减少计算:
- 令 sizeof( query )表示广告请求中的定向标签个数
- 令 sizeof( Conjunction )表示某 Conjunction 的含有 `∈` 的赋值集数目
- 当 sizeof( query )< sizeof( Conjunction )时,该 Conjunction 一定不满足该次请求
- 例如:广告请求只有 2 个标签,对于需要 3 以上标签求 `并` 的广告,肯定不满足此次检索的匹配条件
根据上图的一组广告为例,这组广告的 DNF 可以按如下的方式分解成一些 conjunction
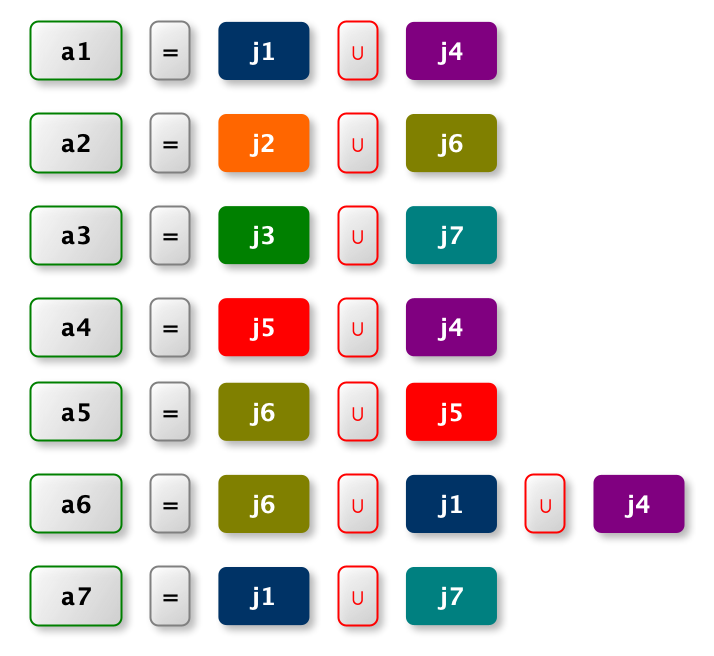
对应的倒排索引很容易地写成下面的的形式:
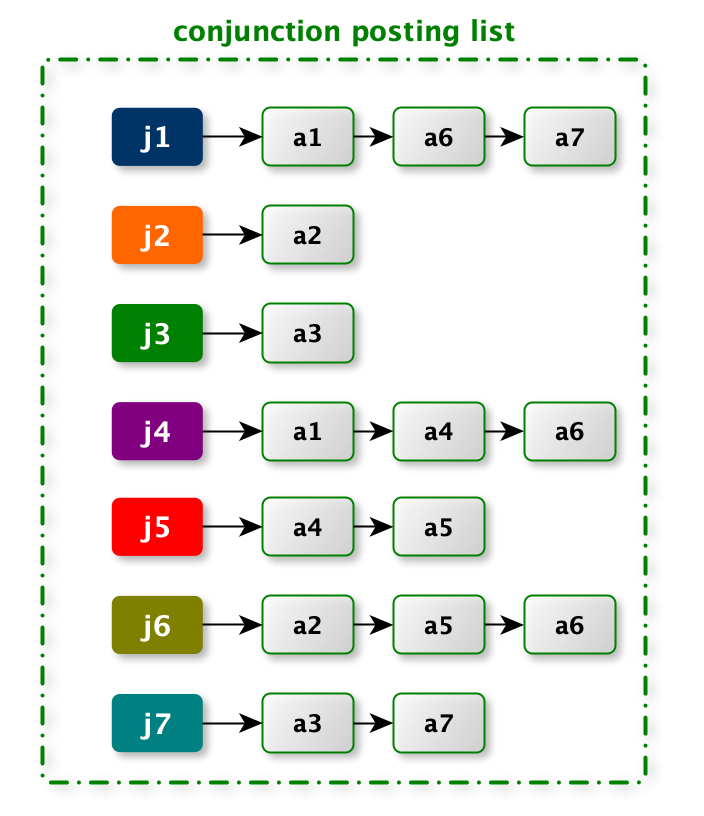
在上述 所有 Conjunction 的最大 size 为 2(Conjunction 的含有 `∈` 的赋值集数目),可以将倒排索引分成 3 部分,每部分中所有
Conjunction 的 size 一样,按照这样的准则,最终形成的 Conjunction 排索引 应为下面的形式:
注意:
- sizeof( Conjunction )= 0,包含那些所有只有 `∉` 操作负的 Conjunction
- 为了保证给定一个 assignment,sizeof( Conjunction )= 0 至少出现在一个倒排表里,算法引入 `Z` 为一个特殊的 term,并且将所有 sizeof( Conjunction )= 0 都放入其倒排表中,并赋以一个 `∈` 操作符。
检索
用户请求范式
为连续的多个(attribute, value) 的二元组来表达,实际上我们也可以将其称为 assignments,或者叫 request assignments
| 用户请求 | 性别 | 地域 | 网络 | 机型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Request1 | 男 | 上海 | wifi | RENO5A51 |
| Request2 | 女 | 杭州 | 5G | FINDX5 |
| … | ||||
| Request3 | 女 | 北京 | 4G | RENO8 |
为连续的多个(attribute, value) 的二元组来表达,实际上我们也可以将其称为 assignments,或者叫 request assignments
令 n = sizeOf( user ),我们仅需要在 Level size <= n 的索引中检索符合条件的 Conjunction id。
假如有 request assignments :{gender=M, City = SZ} , n = 2,因此,我们仅需要在 level size <= 2 的索引中进行查询。即 level 0, level 1, level 2
假如广告主创建了一个广告定向条件对应的 Conjunction size=3,也就是说要满足三个属性∈的条件才能够匹配。
| 例如:c5:Gender ∈ {M} ^ city ∈ {SZ} ^ network ∈ {WIFI,4G} | c5 | = 3 |
一旦检索请求的属性数量小于 3,则无论如何也无法满足 c5 中要求定向的三个条件
高效的 DNF 检索算法
在介绍《Indexing Boolean Expressions》中描述的高效的 DNF 检索算法之前,我们有几个点需要先了解一下,首先是我们需要知道当一个检索请求来了之后,哪些 Conjunction 是符合条件的?假如要进行暴力检索,应该会怎么做?
符合条件的 Conjunction:
什么是符合条件的 Conjunction,对于一个析取范式的合取子句,即 xxx 且 xxx 且 xxx 来说,只有同时满足 3 个条件才算符合条件。由于“xxx”可能是 ∈ 也可能是 ∉,那么对于一个符合条件的 Conjunction 来说,需要保证所有∈的条件均满足,∉的条件均不能满足。
又由于,我们对 Conjunction size 的定义为∈条件的个数,那么最终,我们需要满足:满足 ∈条件的个数 >=Conjunction size 且 满足 ∉条件的个数 <= 0 个。
暴力法找到符合条件的 Conjunction ID
为了找到,满足 ∈ 条件的个数 >= Conjunction size 且 满足 ∉ 条件的个数 <= 0 个 的 Conjunction 。我先用暴力法找到这些 Conjunction
public Set<Integer> search(Map<String, String> userProfiles, Map<Assignment, List<Integer>> postingList, int size) {
List<List<Integer>> includeList = new ArrayList<>();
Set<Integer> excludeSet = new HashSet<>();
// 匹配
for (Assignment assignment : postingList.keySet()) {
String value = userProfiles.get(assignment.getAttr());
if (assignment.getValue().equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
if ("∈".equals(assignment.getPredicate())) {
includeList.add(postingList.get(assignment));
} else {
excludeSet.addAll(postingList.get(assignment));
}
}
}
// 暴力统计
// key:conjunctionId, value:频次
Map<Integer, Integer> conjunctionMap = new HashMap<>();
for (List<Integer> list : includeList) {
for (Integer conjunctionId : list) {
if (excludeSet.contains(conjunctionId)) {
continue;
}
conjunctionMap.put(conjunctionId, conjunctionMap.getOrDefault(conjunctionId, 0) + 1);
}
}
// 过滤
return conjunctionMap.entrySet().stream()
.filter(x -> x.getValue() >= size)
.map(Map.Entry::getKey)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
假设在 size = 2 的第一级倒排表如下
| Key | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| ( gender, 女) | $(j_2,\in)$ |
| ( gender, 男) | $(j_3,\in),(j_4,\in)$ |
| ( geo, 北京) | $(j_2,\in),(j_3,\in),(j_4,\notin)$ |
| ( geo,上海) | $(j_3,\in)$ |
| ( network, WIFI) | $(j_4,\in)$ |
筛选 postingList
一个用户请求,用户标签:`( gender, 男)`,`(city, 北京)`,`(network, WIFI)`,从 size = 2 的索引中匹配到对应的 postingList
| Key | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| ( gender, 女) | $(j_2,\in)$ |
| ( gender, 男) | $(j_3,\in),(j_4,\in)$ |
| ( geo, 北京) | $(j_2,\in),(j_3,\in),(j_4,\notin)$ |
| ( geo,上海) | $(j_3,\in)$ |
| ( network, WIFI) | $(j_4,\in)$ |
结果
| Key | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| ( gender, 男) | $(j_3,\in),(j_4,\in)$ |
| ( geo, 北京) | $(j_2,\in),(j_3,\in),(j_4,\notin)$ |
| ( network, WIFI) | $(j_4,\in)$ |
初始化 postingList
前提:postingList 每一行内部 ,按照 conjunctionId 升序进行排序,当 conjunctionId 相同是,$\notin < \in$。
postingList 每一设置一个 currentEntry,初始化为每行第一个元素,使用下划线标识指针。
| currentIndex | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| 0 | $(\underline{j_3},\underline{\in})$$,(j_4,\in)$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_2},\underline{\in})$$,(j_3,\in),(j_4,\notin)$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_4},\underline{\in})$ |
postingList 之间排序,按照 currentEntry 的大小进行排序。排序规则:conjunctionId 升序进行排序,当 conjunctionId 相同是,$\notin < \in$。
| currentIndex | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| 0 | $(\underline{j_2},\underline{\in})$$,(j_3,\in),(j_4,\notin)$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_3},\underline{\in})$$,(j_4,\in)$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_4},\underline{\in})$ |
整体的排布类似如下图片,小智集中在左上角
循环取数
postingList 目前数据特点
- 每行按照 conjunctionId 升序并且数据不重复。
- 每列按照 conjunctionId 升序,数据重复数最多为 size 个
我们要找的数据是:重复数为 size 的 conjunctionId。如果满足条件,那么第 0 行与第 k -1 行的 currentEntry 必须相等。否则从第 0 行到第 k - 2 所有的 currentEntry 对应的 conjunctionId 的数据都不满足 size 。假设其中有一项满足重复数为 size,那么后续行的 currentEntry 一定与其相等。
因此有两种情况
- 如果 postingList[ 0 ].currentEntry == postingList[ k - 1 ].currentEntry,那么 postingList[ 0 ].currentEntry 对应 conjunctionId,满足条件,放入最终返回的集合中。nextId ++(为重置 前 k 行的 currentEntry 做准备)。
- 如果 postingList[ 0 ].currentEntry != postingList[ k - 1 ].currentEntry,那么 postingList[ 0 ].currentEntry 对应 conjunctionId,不满足条件。nextId = postingList[ k - 1 ].currentEntry
不相等
如下图:postingList[ 0 ][ currentIndex] != postingList[ size - 1 ][ currentIndex]
将第 1 到第 k - 1 行 skip to 到第 k -1 行currentEntry 对应 conjunctionId(第一个小于等于)的位置
| currentIndex | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| 0 | $(\underline{j_2},\underline{\in})$$,(j_3,\in),(j_4,\notin)$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_3},\underline{\in})$$,(j_4,\in)$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_4},\underline{\in})$ |
将第 1 到第 k - 1 行 skip to 到第 k -1 行currentEntry 对应 conjunctionId(第一个小于等于)的位置。
相等
更新完毕 currentEntry 后,对 postingList 重新排序
| currentIndex | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| 1 | $({j_2},\in)$,$(\underline{j_3},\underline{\in})$,$(j_4,\notin)$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_3},\underline{\in})$$,(j_4,\in)$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_4},\underline{\in})$ |
这一轮:如上图:postingList[ 0 ][ currentIndex] == postingList[ size - 1 ][ currentIndex] ,那么 conjunctionId 满足条件。
将第 1 到第 k - 1 行 skip to 到后一个位置
相等且$\notin$
更新完毕 currentEntry 后,对 postingList 重新排序
| currentIndex | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| 2 | $({j_2},\in),(j_3,\in)$,$(\underline{j_4},\underline{\notin})$ |
| 1 | $(j_3,\in)$,$(\underline{j_4},\underline{\in})$ |
| 0 | $(\underline{j_4},\underline{\in})$ |
如上图:postingList[ 0 ][ currentIndex] = $(j_4,\notin)$、postingList[ k-1 ][ currentIndex] = $(j_4,\in)$,$j_4$ 是我们认为不满足条件的 Conjunction,并将所有 $j_4$ 的 currentEntry skip to 到 next entry(currentIndex++)
更新完毕 currentEntry 后,对 postingList 重新排序
跳出循环
PostingLists[level - 1] .currentEntry=NULL 跳出循环
| currentIndex | PostingList(Entries) |
|---|---|
| 3 | $({j_2},\in),(j_3,\in),(j_4,\notin)$,$\underline{NULL}$ |
| 2 | $(j_3,\in),(j_4,\in)$,$\underline{NULL}$ |
| 1 | $(\underline{j_4},\underline{\in})$,$\underline{NULL}$ |
工程实现
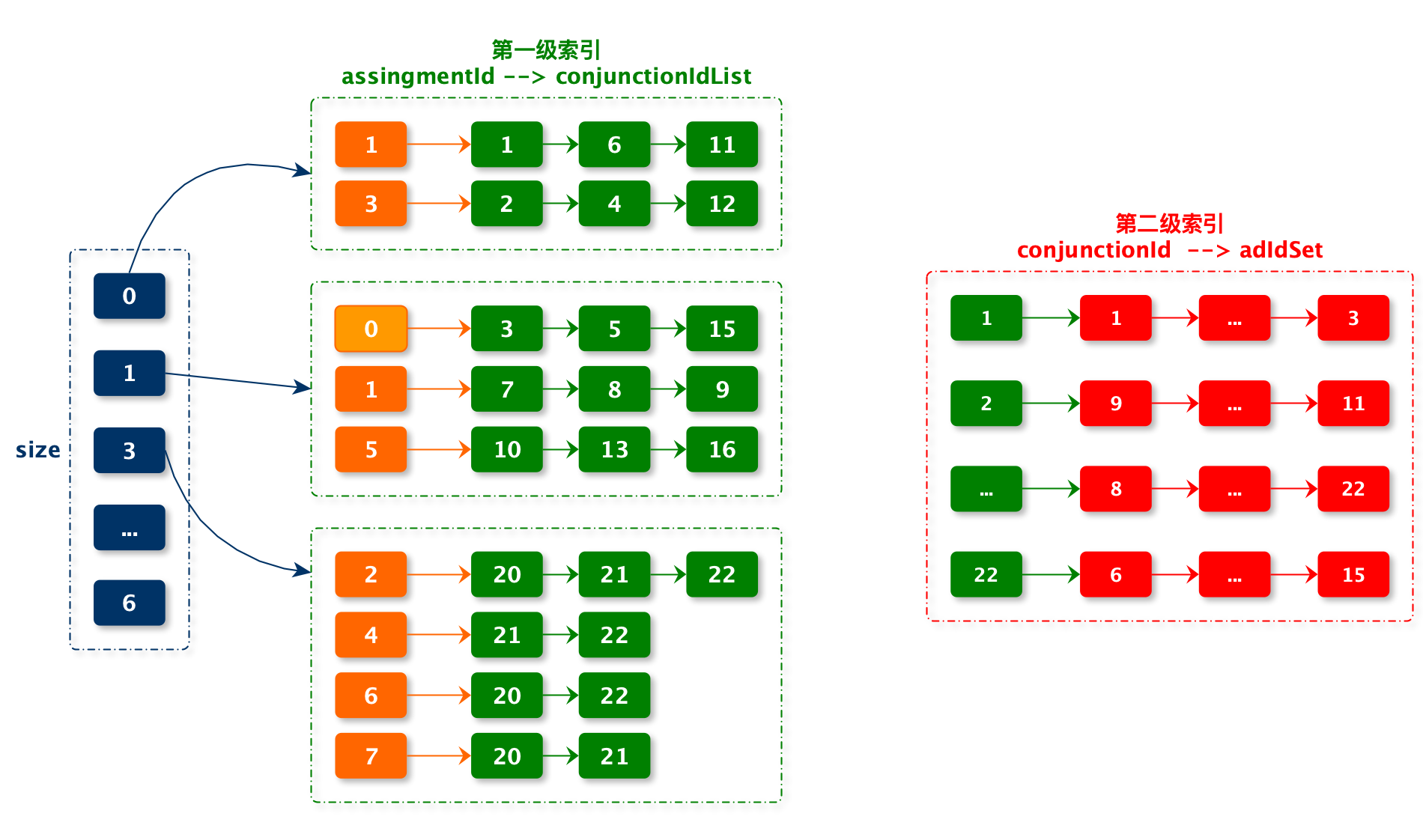
索引设计
在工程实现时,会对 conjunction 和 assignment 进行 id 化。并且不同广告使用相同 conjunction 和 assignment 会公用 id 。
下边代码:
- index :第一级索引
- conjId2AdIdListMap:第二级索引
@Slf4j
@Data
public class DNFInvertedIndex implements Serializable {
// size --> assignmentId --> conjunctionIdList
private Map<Integer, Map<Integer, List<Integer>>> index = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
// conjunctionId --> adIdSet
private Map<Integer, Set<String>> conjId2AdIdListMap = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
}
注意
- size = 0 中存储都是排除定向条件
- size = 1 中有一个特殊定向条件:assignmentId = 0。这个是针对只有排除定向条件没有包含定向条件的广告。也就是之前所说的
Z定向条件 - 在 conjunctionIdList 中 id 是重复的,并且一般都是升序组织数据
- 在 conjunctionIdList 中 id 的重复个数最多等于 size 。
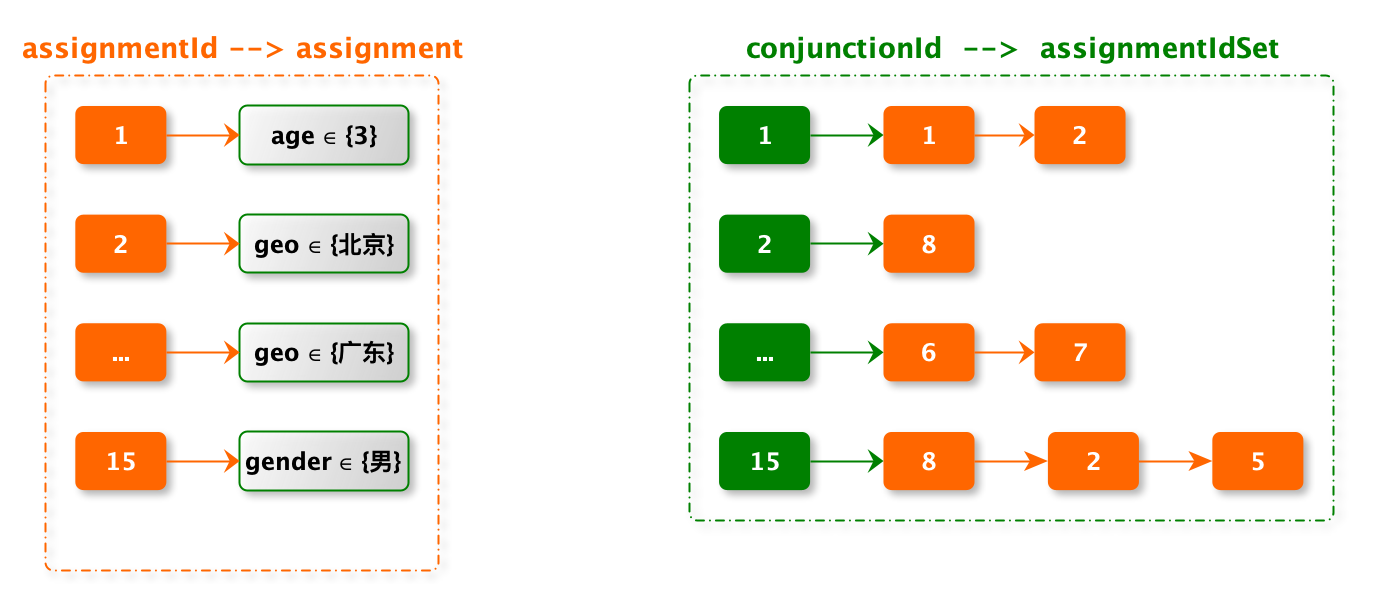
- assignId2KeyMap:存储 assignmentId 与原始的 assignment。在检索时需要 assignment 与用户标签匹配
- conjId2AssignIdMap:conjunction 包含的 assignment
// assignmentId --> assignment
private Map<Integer, Assignment> assignId2KeyMap = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
// conjunctionId --> assignmentIdSet
private Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> conjId2AssignIdMap = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
- adId2ConjIdMap:存储广告定向条件,adId 到 conjunction 的映射。由于我们公司定向条件没有多个 conjunction,因此实现时为了简单,没有使用 set 集合
- userHitAssignCache:缓存用户标签与 Assignment 的匹配结果,加速之后的匹配性能。由于一个广告系统,常见定向条件和用户标签的组合的数量级是非常小的。因此可以使用缓存进行加速。
// adId --> conjunctionId
private Map<String, Integer> adId2ConjIdMap = Maps.newConcurrentMap();
private Cache<String, Boolean> userHitAssignCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000000)
.build();
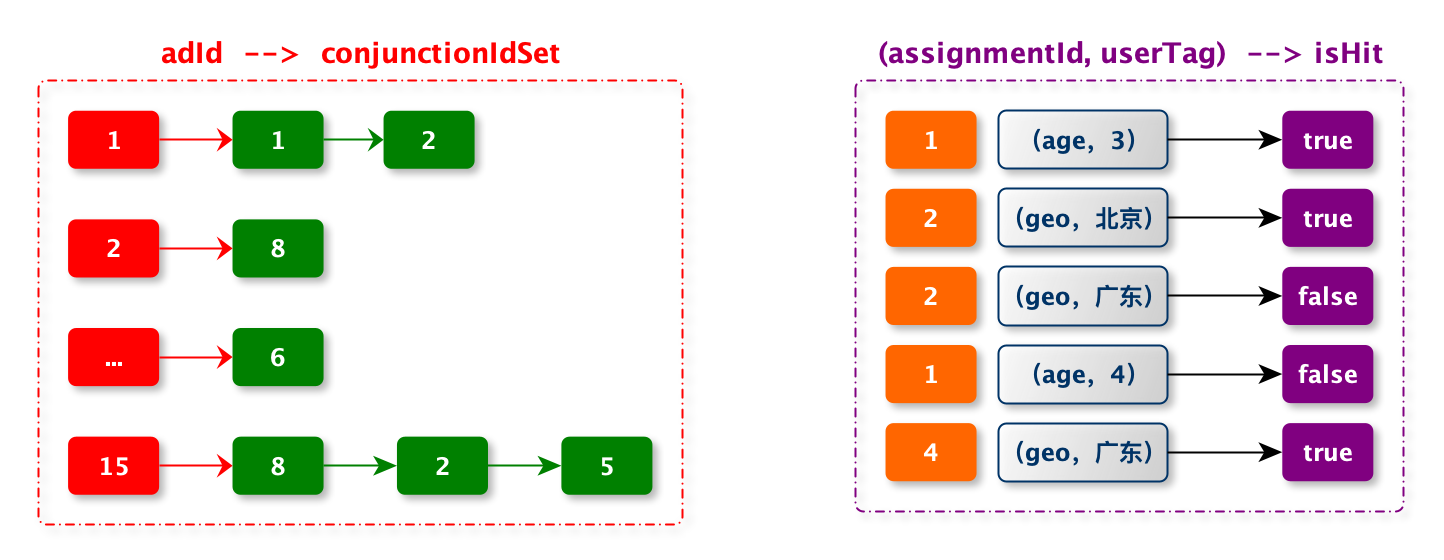
索引构建
// assignmentSet 是广告一个 conjunction 包含的所有定向条件
public void index(String adId, Set<Assignment> assignmentSet) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(assignmentSet)) {
return;
}
Set<Integer> assignIdSet = assignmentSet.stream().map(Assignment::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
int conjId = getConjunctionId(assignIdSet);
// 包含定向条件
Set<Integer> includedAssignIdSet = assignmentSet.stream().filter(Assignment::isIncludeBase).map(Assignment::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// 排除定向条件
Set<Integer> excludedAssignIdSet = assignmentSet.stream().filter(x -> !x.isIncludeBase()).map(Assignment::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// Z 定向条件处理
if (includedAssignIdSet.isEmpty()) {
includedAssignIdSet.add(IndexingFacade.Z_ASSIGN_ID);
assignIdSet.add(IndexingFacade.Z_ASSIGN_ID);
}
addIndex(includedAssignIdSet.size(), includedAssignIdSet, conjId);
addIndex(0, excludedAssignIdSet, conjId);
maxSize = Math.max(maxSize, includedAssignIdSet.size());
adId2ConjIdMap.put(adId, conjId);
conjId2AdIdListMap.computeIfAbsent(conjId, x -> Sets.newConcurrentHashSet()).add(adId);
if (!conjId2AssignIdMap.containsKey(conjId)) {
conjId2AssignIdMap.put(conjId, assignIdSet);
}
}
// 添加索引
public void addIndex(int size, Set<Integer> assignIdSet, int conjId) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(assignIdSet)) {
return;
}
assignIdSet.forEach(assignId -> {
List<Integer> conjIdList = index
.computeIfAbsent(size, x -> Maps.newConcurrentMap())
.computeIfAbsent(assignId, y -> Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList());
IndexUtils.addSorted(conjIdList, conjId);
});
}
// 获取或者生成 conjunctionId
private int getConjunctionId(Set<Integer> assignIdSet) {
Optional<Integer> existingId = conjId2AssignIdMap.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> entry.getValue().equals(assignIdSet))
.map(Map.Entry::getKey)
.findFirst();
if (existingId.isPresent()) {
return existingId.get();
}
maxConjunctionId++;
return maxConjunctionId;
}
检索
入参是用户标签
- 第一阶段:获取匹配的 conjunctionId
- 第一步是处理用户标签,过滤掉没有定向的标签,将标签内容转换为 set 集合(与调用多个值以英文逗号分割)
- 在第一级索引中,从大到小遍历每一层索引进行检索。注意当 size == 0 中存储的是排除定向条件以及 size == 1 中存储着定向条件
Z - 检查用户标签与 Assignment 是否匹配
- 如果匹配,暂时获取 Assignment 对应 conjunctionIdList
- 如果不匹配,跳过
- 统计每个匹配的 Assignment 对应 conjunctionIdList 中的 conjunctionId 重复个数,如果重复个数达到该层 size 数,那么 conjunctionId 就是符合条件
- 这里有三种算法:后续会对三种算法进行测试
- 暴力统计,通过两层循环遍历所有数据,统计 conjunctionId 的重复数
- 多路归并统计
- 论文中提到 DNF 检索算法
- 这里有三种算法:后续会对三种算法进行测试
- 第二阶段:根据 conjunctionId 查找到对应的 adId
- 从 conjId2AdIdListMap 中直接获取 adId
public List<String> search(Map<String, String> userProfile) {
Map<String, Set<String>> hitFiledMap = IndexUtils.extractAssignValue(userProfile, assignNameSet);
int count = hitFiledMap.size();
Set<Integer> hitConIdSet = new HashSet<>();
DebugUtils.log(userProfile, "maxSize:{},hitFiledMap:{}", maxSize, hitFiledMap);
// hit assign
for (int size = Math.min(maxSize, count); size >= 0; size--) {
if (size > count || !index.containsKey(size)) {
continue;
}
// assignId --> conjunctionIdList
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> assignId2ConIdList = index.get(size);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(assignId2ConIdList) || assignId2ConIdList.size() < size) {
continue;
}
if (size == 0) {
hitConIdSet.removeAll(hitConjunctionId(hitFiledMap, assignId2ConIdList, size, userProfile));
continue;
}
hitConIdSet.addAll(hitConjunctionId(hitFiledMap, assignId2ConIdList, size, userProfile));
}
// 获取广告
return hitConIdSet.stream()
.filter(conjId2AdIdListMap::containsKey)
.flatMap(conId -> conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conId).stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private Set<Integer> hitConjunctionId(Map<String, Set<String>> hitFiledMap, Map<Integer, List<Integer>> assignId2ConIdList, int size, Map<String, String> userProfile) {
Set<Integer> hitAssignIdSet = hitAssignSet(hitFiledMap, assignId2ConIdList, userProfile);
DebugUtils.log(userProfile, "size:{},hitAssignIdSet:{}", size, hitAssignIdSet);
if (hitAssignIdSet.size() < size) {
return new HashSet<>();
}
List<Integer[]> conjunctionIdList = hitAssignIdSet.stream().map(assignId2ConIdList::get).map(x -> x.toArray(new Integer[0])).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 统计命中的 conjunctionId 个数
Map<Integer, Integer> conjunctionIdCountMap = IndexUtils.statsCount(conjunctionIdList, size);
// 过滤小于 size 的 conjunctionId
Set<Integer> res = conjunctionIdCountMap.keySet().stream().filter(conId -> conjunctionIdCountMap.get(conId) >= size).collect(Collectors.toSet());
DebugUtils.log(userProfile, "size:{},conjunctionIdCountMap:{},hitConjunctionId:{}", size, conjunctionIdCountMap, res);
return res;
}
public Set<Integer> hitAssignSet(Map<String, Set<String>> hitFiledMap, Map<Integer, List<Integer>> assignId2ConIdList, Map<String, String> userProfile) {
Set<Integer> res = new HashSet<>(hitFiledMap.size());
for (Integer assignId : assignId2ConIdList.keySet()) {
if (assignId == IndexingFacade.Z_ASSIGN_ID) {
res.add(assignId);
continue;
}
if (!assignId2AssignMap.containsKey(assignId)) {
continue;
}
Assignment assignment = assignId2AssignMap.get(assignId);
if (!hitFiledMap.containsKey(assignment.getName())) {
continue;
}
Set<String> userTags = hitFiledMap.get(assignment.getName());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(userTags)) {
if (userProfileHitAssign(userTags, assignment)) {
res.add(assignId);
}
continue;
}
String cacheKey = getCacheKey(assignment.getName(), userProfile.get(assignment.getName()), assignId);
Boolean isHit = hitAssignCache(cacheKey);
if (isHit != null) {
if (isHit) {
res.add(assignId);
}
continue;
}
isHit = userProfileHitAssign(userTags, assignment);
userHitAssignCache.put(cacheKey, isHit);
if (isHit) {
res.add(assignId);
}
}
return res;
}
public Boolean hitAssignCache(String cacheKey) {
return userHitAssignCache.getIfPresent(cacheKey);
}
public String getCacheKey(String key, String value, Integer assignId) {
return key + "|" + value + "|" + assignId;
}
public boolean userProfileHitAssign(Set<String> userFiledData, Assignment assignment) {
if (!assignment.isIncludeBase() && userFiledData.isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
return assignment.getOperatorEnum().operate(OperatorImpl.builder()
.userProfileValues(userFiledData)
.assignValues(assignment.getValues())
.assignment(assignment)
.build());
}
动态更新
对于广告信息的变更,对应的索引也需要跟随更新。
主要变更有:
- 广告的新增
- 广告的更新
- 广告位变化
- 定向广告变为通投广告
- 广告定向条件的新增、修改、删除
- 广告的删除或下线
- 广告投放单元删除
- 广告相关数据的删除:广告投放计划、广告素材、广告渠道包等
由于广告业务变更比较复杂,不在这里一一说明,接下来重点说一下索引层的变化
索引层主要是分三类:
- 索引新增:在索引创建那里已经说明了
- 索引更新:这个是最复杂的
- 索引删除
索引更新
- 如果新旧定向条件没有变化,就不需要处理
- 如果 conjunctionId 是独占,那么可以继续使用 conjunctionId,只是 conjunctionId 对应 assignment 变化了。需要修正对
- 继续修第一级索引。
- 判断新的 Include 定向集合数与旧的 Include 定向集合数是否相等。
- 如果相等,在第一级索引同一层级内删除新 include 中没有定向条件,新增新 Include 定向条件有但是旧 Include 定向条件没有的数据
- 如果不相等,那么新旧定向条件不在同一层级,只需要在删除旧层级的数据,在新层级中新增数据即可。
- 如果 conjunctionId 是共享,说明还有其他广告在使用 conjunctionId,以及 conjunctionId 对应 assignment。既然新增当前广告的定向条件变了,那么就不能再当前的 conjunctionId,需要根据当前的定向条件查找对应 的 conjunctionId,如果没有需要生成一个新的 conjunctionId。
- 由于其他广告还在使用 conjunctionId,应 conjunctionId 对应的定向数据不需要修改。只需要将 conjunctionId 与广告相关的数据清除。
- 然后再新 conjunctionId 只需要新增数据即可。
public boolean update(IndexItem indexItem) {
String adId = indexItem.getId();
int conjId = adId2ConjIdMap.get(adId);
Set<Integer> oldAssignIdSet = conjId2AssignIdMap.get(conjId);
Set<Integer> newAssignIdSet = indexItem.getAssignmentSet().stream().map(Assignment::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// 定向条件没有变化
if (oldAssignIdSet.equals(newAssignIdSet)) {
return true;
}
Set<Integer> newIncludeAssignSet = indexItem.getAssignmentSet().stream().filter(Assignment::isIncludeBase).map(Assignment::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set<Integer> newExcludeAssignSet = indexItem.getAssignmentSet().stream().filter(key -> !key.isIncludeBase()).map(Assignment::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
if (newIncludeAssignSet.isEmpty()) {
newIncludeAssignSet.add(IndexingFacade.Z_ASSIGN_ID);
newAssignIdSet.add(IndexingFacade.Z_ASSIGN_ID);
}
// 当前广告独占 conjId,此时可以复用 conjId
if (conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId).size() == 1 && conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId).contains(adId)) {
log.info("index_update 独占 adId:{},conjId:{},newKeyIds:{},oldKeyIds:{}", indexItem.getId(), conjId, newAssignIdSet, oldAssignIdSet);
Set<Assignment> oldAssignmentSet = oldAssignIdSet.stream().filter(x -> assignId2AssignMap.containsKey(x)).map(x -> assignId2AssignMap.get(x)).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set<Integer> oldIncludeAssignSet = oldAssignmentSet.stream().filter(Assignment::isIncludeBase).map(Assignment::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set<Integer> oldExcludeAssignSet = oldAssignmentSet.stream().filter(key -> !key.isIncludeBase()).map(Assignment::getId).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// 更新 size
updateAssignSet(oldIncludeAssignSet, newIncludeAssignSet, conjId, oldIncludeAssignSet.size(), newIncludeAssignSet.size());
updateAssignSet(oldExcludeAssignSet, newExcludeAssignSet, conjId, 0, 0);
conjId2AssignIdMap.put(conjId, newAssignIdSet);
} else {
// 生成新的 newConjId,重新插入,旧的 conjId 其他广告使用,不需要处理
int newConjId = getConjunctionId(newAssignIdSet);
log.info("index_update 非独占 adId:{},newConjId:{},oldConjId:{},newKeyIds:{},oldKeyIds:{},otherAdId:{}", indexItem.getId(), newConjId, conjId, newAssignIdSet, oldAssignIdSet, conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId));
addIndex(newIncludeAssignSet.size(), newIncludeAssignSet, newConjId);
addIndex(0, newExcludeAssignSet, newConjId);
conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId).remove(adId);
conjId2AdIdListMap.computeIfAbsent(newConjId, x -> Sets.newConcurrentHashSet()).add(adId);
adId2ConjIdMap.put(adId, newConjId);
conjId2AssignIdMap.put(newConjId, newAssignIdSet);
}
if (newIncludeAssignSet.size() > maxSize) {
maxSize = getNewMaxSize();
}
return true;
}
public void updateAssignSet(Set<Integer> oldAssignSet, Set<Integer> newAssignSet, int conjId, int oldSize, int newSize) {
if (oldSize != newSize) {
addIndex(newSize, newAssignSet, conjId);
removeIndex(oldSize, oldAssignSet, conjId);
} else {
Pair<Set<Integer>, Set<Integer>> assignDiff = IndexUtils.compareSets(oldAssignSet, newAssignSet);
Set<Integer> addedAssignIdSet = assignDiff.getLeft();
Set<Integer> removedAssignIdSet = assignDiff.getRight();
addIndex(newSize, addedAssignIdSet, conjId);
removeIndex(newSize, removedAssignIdSet, conjId);
}
}
public void addIndex(int size, Set<Integer> assignIdSet, int conjId) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(assignIdSet)) {
return;
}
assignIdSet.forEach(assignId -> {
List<Integer> conjIdList = index
.computeIfAbsent(size, x -> Maps.newConcurrentMap())
.computeIfAbsent(assignId, y -> Lists.newCopyOnWriteArrayList());
IndexUtils.addSorted(conjIdList, conjId);
});
}
索引删除
由于 conjunctionId 和 assignmentId 在不同广告之间重复使用,因此需要判断 conjunctionId 和 assignmentId 是独占还是共享的
- 如果是独占的,在删除时,即可清除数据。
- 如果是共享的,在删除时,不能清除 conjunctionId 相关的数据,只能清除与 广告id,最直接相关的数据。
public boolean remove(String adId) {
if (!adId2ConjIdMap.containsKey(adId)) {
return false;
}
int conjId = adId2ConjIdMap.get(adId);
// 清理 conjunctionId --> adIdList
if (conjId2AdIdListMap.containsKey(conjId) && conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId).contains(adId)) {
conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId).remove(adId);
if (conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId).isEmpty()) {
conjId2AdIdListMap.remove(conjId);
}
}
// adId --> conjunctionId
adId2ConjIdMap.remove(adId);
// conjunctionId 非独占
if (conjId2AdIdListMap.containsKey(conjId)) {
log.info("index_delete 非独占 adId:{},conjId:{},keyIds:{},otherAdIds:{}", adId, conjId, conjId2AssignIdMap.get(conjId), conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId));
return true;
}
log.info("index_delete 独占 adId:{},conjId:{},keyIds:{},otherAdIds:{}", adId, conjId, conjId2AssignIdMap.get(conjId), conjId2AdIdListMap.get(conjId));
// 清理 size --> assignId --> conjunctionIdList
if (conjId2AssignIdMap.containsKey(conjId)) {
Set<Integer> assignIdSet = conjId2AssignIdMap.get(conjId);
Set<Integer> includeAssignIdSet = assignIdSet.stream()
.filter(x -> assignId2AssignMap.containsKey(x) && assignId2AssignMap.get(x).isIncludeBase())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set<Integer> excludeAssignIdSet = assignIdSet.stream()
.filter(x -> assignId2AssignMap.containsKey(x) && !assignId2AssignMap.get(x).isIncludeBase())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
removeIndex(includeAssignIdSet.size(), includeAssignIdSet, conjId);
removeIndex(0, excludeAssignIdSet, conjId);
// 清理 conjunctionId --> assignIdSet
conjId2AssignIdMap.remove(conjId);
}
maxSize = getNewMaxSize();
return true;
}
public void removeIndex(int size, Set<Integer> assignIdSet, int conjId) {
if (!index.containsKey(size) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(assignIdSet)) {
return;
}
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> assignId2ConIdList = index.get(size);
assignIdSet.stream()
.filter(assignId2ConIdList::containsKey)
.peek(assignId -> index.get(size).get(assignId).removeIf(x -> x == conjId))
.filter(assignId -> index.get(size).get(assignId).isEmpty())
.forEach(assignId2ConIdList::remove);
if (assignId2ConIdList.isEmpty()) {
index.remove(size);
}
}
三种算法性能测试
暴力算法统计
public static Set<Integer> forceStatsCount(List<Integer[]> list, int size) {
Map<Integer, Integer> res = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer[] integers : list) {
for (Integer integer : integers) {
res.put(integer, res.getOrDefault(integer, 0) + 1);
}
}
return res.entrySet().stream().filter(e -> e.getValue() >= size).map(Map.Entry::getKey).collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
多路归并统计
public static Set<Integer> mergeStatsCount(List<Integer[]> list, int size) {
int n = list.size(); // 数组的数量
int[] pointers = new int[n]; // 每个数组的指针
Map<Integer, Integer> countMap = new HashMap<>(100); // 存储每个数的出现次数
while (true) {
int minElement = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// 选取本轮最小值:minElement
int doneCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (pointers[i] < list.get(i).length) {
minElement = Math.min(minElement, list.get(i)[pointers[i]]);
} else {
doneCount++;
}
}
if (n - doneCount < size || doneCount == n) {
break;
}
// 统计 minElement 出现次数
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (pointers[i] < list.get(i).length && list.get(i)[pointers[i]] == minElement) {
count++;
pointers[i]++;
}
}
countMap.put(minElement, countMap.getOrDefault(minElement, 0) + count);
}
return countMap.entrySet().stream().filter(e -> e.getValue() >= size).map(Map.Entry::getKey).collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
DNF 检索算法
- 没选取一条数据需要对 data 排序
public static Set<Integer> statsCount(List<MutablePair<Integer, Integer[]>> data, int size) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
// 排序
data.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> {
if (o.getLeft() < o.getRight().length) {
return o.getRight()[o.getLeft()];
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}));
boolean isMatch = false;
while (data.get(size - 1).getLeft() < data.get(size - 1).getRight().length) {
Integer nextId = data.get(size - 1).getRight()[data.get(size - 1).getLeft()];
// conjunctionId 个数是否等于 size
if (data.get(0).getRight()[data.get(0).getLeft()].equals(nextId)) {
set.add(data.get(0).getRight()[data.get(0).getLeft()]);
nextId += 1;
isMatch = true;
}
// 调整data 中每个数据的:currentId
skipTo(data, nextId, isMatch, size);
data.removeIf(x -> x.getLeft() >= x.getRight().length);
if (data.size() < size) {
break;
}
// 排序
data.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> {
if (o.getLeft() < o.getRight().length) {
return o.getRight()[o.getLeft()];
}
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}));
}
return set;
}
public static void skipTo(List<MutablePair<Integer, Integer[]>> data, int targetId, boolean isMatch, int size) {
// 上次匹配成功,只需要修改前 size 个 MutablePair
if (isMatch) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
data.get(i).setLeft(data.get(i).getLeft() + 1);
}
return;
}
// 修改全部
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 找到最近一个比 targetId 大的下标,注意:data.getRight() 是有序的
int index = IndexUtils.indexedBinarySearch(data.get(i).getRight(), targetId, data.get(i).getLeft(), data.get(i).getRight().length-1);
// 找到与 targetId 下标相等
if (index >= 0) {
data.get(i).setLeft(index);
} else {
data.get(i).setLeft(-index - 1);
}
}
}
对数器
public static void main(String[] args) {
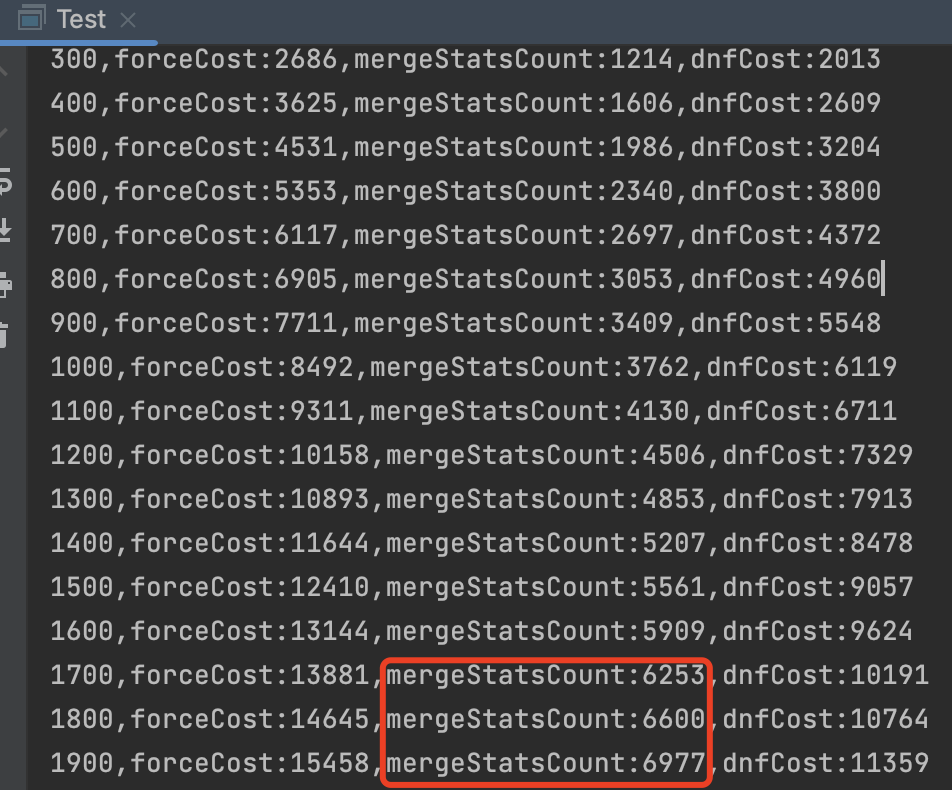
long forceCost = 0;
long onlineCost = 0;
long dnfCost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
int size = 30;
List<Integer[]> mockListData = mockData(10000, size);
List<MutablePair<Integer, Integer[]>> data = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < mockListData.size(); j++) {
data.add(MutablePair.of(0, mockListData.get(j)));
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Set<Integer> res2 = forceStatsCount(mockListData, size);
forceCost += System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Set<Integer> res3 = mergeStatsCount(mockListData, size);
onlineCost += System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Set<Integer> res1 = dnfStatsCount(data, size);
dnfCost += System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
if (!res1.equals(res3) || !res1.equals(res2)) {
System.out.println("ERROR");
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
}
if (i % 100 == 0) {
System.out.println(i + ",forceCost:" + forceCost + ",mergeStatsCount:" + onlineCost + ",dnfCost:" + dnfCost);
}
}
System.out.println("Over");
}
public static List<Integer[]> mockData(int count, int size) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
while (set.size() < size) {
set.add(random.nextInt(30));
}
for (Integer keyId : set) {
map.computeIfAbsent(keyId, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(i);
}
}
List<Integer[]> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (List<Integer> value : map.values()) {
res.add(value.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o)).toArray(Integer[]::new));
}
return res.stream().limit(size + 1).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
从最终结果来看,多路归并统计算法效果最好。