查并集
背景
问题:
- 在 O(1) 的时间复杂度的情况下,判断 a 和 b 是否属于同一个集合。
- 在 O(1) 的时间复杂度的情况下,将集合 A 和集合 B 数据合并。
尝试使用已有数据结构尝试解决上述问题
HashSet
要满足问题 1,使用 HashSet,可以在 O(1) 判断 a 和 b 是否属于同一个集合。但是要合并集合 A 和集合 B 时,必须将集合 A 中数据拷贝到集合 B 中,或者将集合 B 中数据拷贝到集合 A 中,就达不到 O(1)
LinkedList
如果是链表存储,可以实现在 O(1) 的时间复杂度上合并两个集合。但是在判断 a 和 b 是否属于同一个集合,就需要遍历链表了。
为了更好解决上述两个问题,设计了一个新的数据结构:并查集。
实现
并查集使用向上指的树或者图的结构。最上边的节点是集合代表节点。
主要操作:
- isSameSet( a , b ):判断 a 和 b 是否属于同一个集合。
- unoin( a , b):把两个不相交的集合合并为一个集合。将数据小的集合挂在数据大代表节点下。
下图是并查集的构建过程
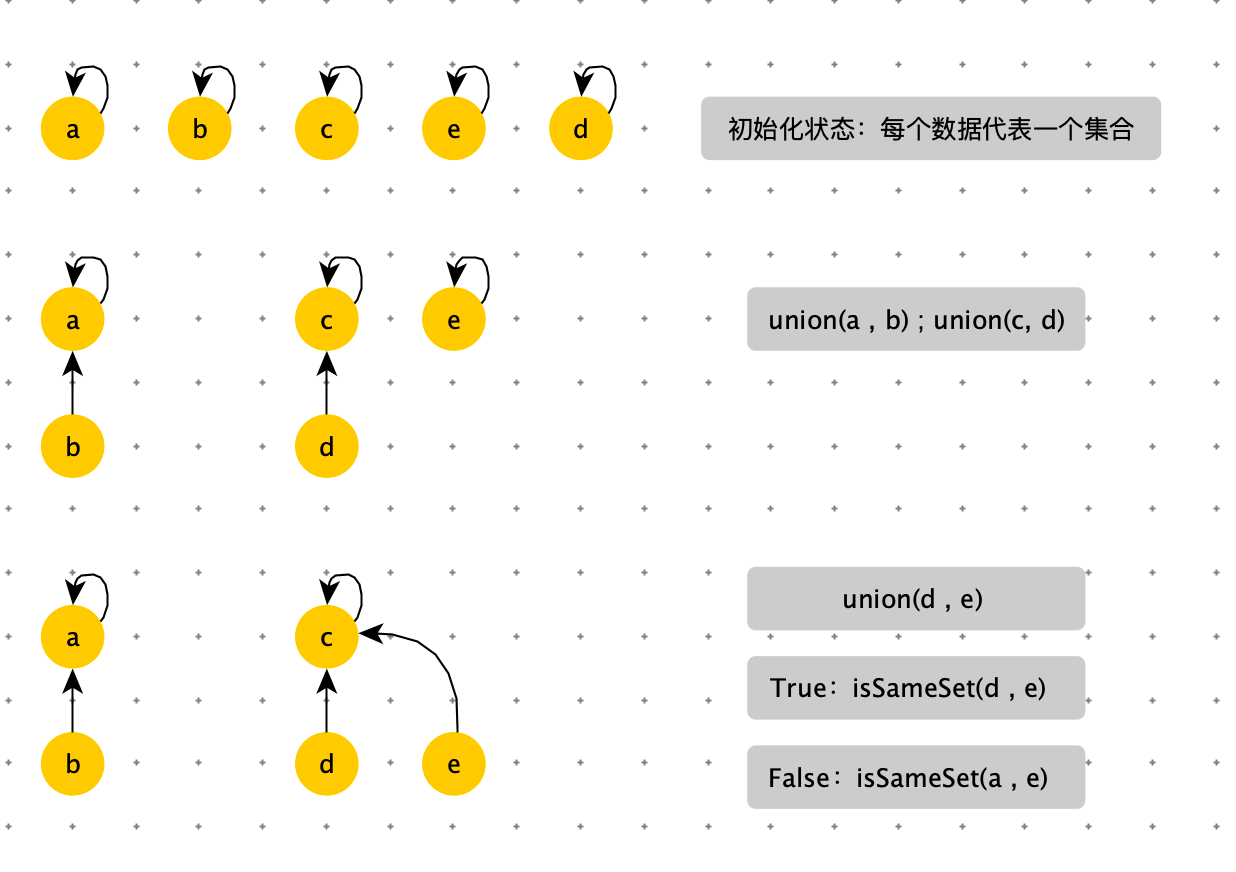
并查集在 union 过程确实是 O(1)。
路径压缩
在 isSameSet 过程中,如果链比较长,不是 O(1)。因此有下边的优化过程,在 isSameSet 时,我们需要从当前节点向上找到代表节点,这个过程中,需要将路径上所有节点之间指向代表节点。如下图:
据研究表明:如果并查集中的数据量为 N,调用 N 次以上的 isSameSet 后,isSameSet 的耗时就是 O(1)
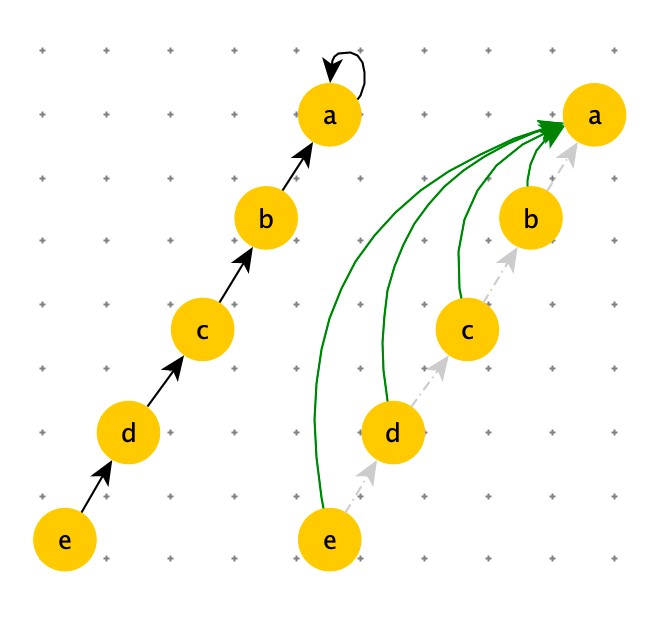
'''
代码最简版查并集
'''
class DisjointSet:
def __init__(self,array):
self.parent = dict((item, item) for item in array)
def find(self, x):
if self.parent[x] != x:
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent, self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def union(self, x, y):
self.parent[self.find(x)] = self.find(y)
def same(self, x, y):
return self.find(x) == self.find(y)
'''
在 find 时压缩路径
'''
class DisjointSet:
def __init__(self, array):
self.father = dict((item, item) for item in array)
def find(self, x):
if self.father[x] == x:
return x
# 记录查找路径
path = []
while self.father[x] != x:
path.append(x)
x = self.father[x]
# 压缩路径,将路径上节点全部指向代表节点
while path:
self.father[path.pop()] = x
return x
def union(self, x, y):
self.father[self.find(x)] = self.find(y)
def same(self, x, y):
return self.find(x) == self.find(y)
'''
在 find 和 union 时压缩路径
'''
class DisjointSet:
def __init__(self, array):
self.father = dict((item, item) for item in array)
self.size_map = dict((item, 1) for item in array)
def find(self, x):
if self.father[x] == x:
return x
path = []
while self.father[x] != x:
path.append(x)
x = self.father[x]
while path:
self.father[path.pop()] = x
return x
def union(self, x, y):
x_parent = self.find(x)
y_parent = self.find(y)
more_parent = x_parent if self.size_map[x_parent] > self.size_map[y_parent] else y_parent
less_parent = x_parent if more_parent == y_parent else y_parent
self.father[less_parent] = more_parent
self.size_map[more_parent] += self.size_map[less_parent]
self.size_map.pop(less_parent)
def same(self, x, y):
return self.find(x) == self.find(y)
disjointSet = DisjointSet([1, 2, 2, 3, 4])
disjointSet.union(1, 2)
print(disjointSet.father)
disjointSet.union(1, 3)
print(disjointSet.father)
disjointSet.union(1, 4)
print(disjointSet.father)
应用并查集
判断图是否有环
需要定义如何表示集合。一种常用的策略是为每个集合选定一个固定的元素,称为代表,以表示整个集合。接着 Find(x) 返回 xx 所属集合的代表,而 Union 使用两个集合的代表作为参数。
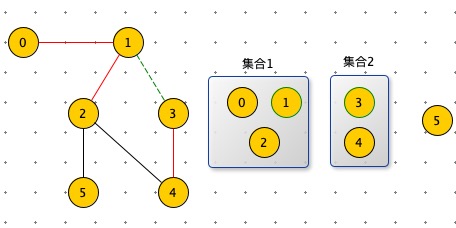
边(1,3),是集合1 与 集合 2 融合。

如图:红线的变表示已经已经处理过的边。节点 0,1,2,3,4 是联通的,在一个集合中。
节点 2,4 已经在同一个集合中了,那么边(2,4)就表示有环。
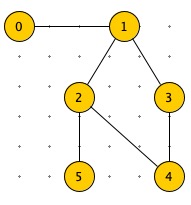
如何实现:集合合并。
使用 parent 数组,表示树的结构。
'''
并查集
主要用途是判断图中是否有环
'''
def find_root(x, parent):
x_root = x
while parent[x_root]:
x_root = parent[x_root]
return x_root
'''
:return 1 合并成功
:return 0 合并失败:x,y 在同一个集合里,既:x_root == y_root
'''
def union(x, y, parent):
x_root = find_root(x, parent)
y_root = find_root(y, parent)
if x_root == y_root:
return False
else:
parent[x_root] = y_root
return True
def main():
edges = [(0, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (3, 4), (2, 5)]
# edges = [(0, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4), (2, 5)]
n = len(edges)
parent = [None] * 6
for i in range(n):
x, y = edges[i]
if not union(x, y, parent):
print("Cycle detected")
return
print("No cycles found")
main()
以上算法在union 中:parent[x_root] = y_root ,随意指定父节点。会导致parent 这可树太长。
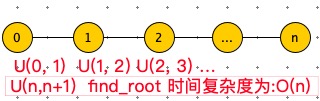
通过 rank 数组存在的是以 i 为根节点,树的高度。
'''
并查集:新增rank,防止在 union 时,过长
主要用途是判断图中是否有环
'''
def find_root(x, parent):
x_root = x
while parent[x_root]:
x_root = parent[x_root]
return x_root
'''
:return 1 合并成功
:return 0 合并失败:x,y 在同一个集合里,既:x_root == y_root
'''
def union(x, y, parent, rank):
x_root = find_root(x, parent)
y_root = find_root(y, parent)
if x_root == y_root:
return False
else:
# parent[x_root] = y_root
if rank[x_root] > rank[y_root]:
parent[y_root] = x_root
elif rank[x_root] < rank[y_root]:
parent[x_root] = y_root
else:
parent[x_root] = y_root
rank[y_root] += 1
return True
def main():
# edges = [(0, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (3, 4), (2, 5)]
edges = [(0, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 4), (3, 4), (2, 5)]
n = len(edges)
parent = [None] * 6
rank = [0] * 6
for i in range(n):
x, y = edges[i]
if not union(x, y, parent, rank):
print("Cycle detected")
return
print("No cycles found")
main()
