概述
有序表的简单介绍
有序表和哈希表的本质区别就是:哈希表的 Key 是通过 Hash 函数散列组织的,而有序表的 Key 是顺序组织的。
- 有序表在使用层面上可以理解为一种**集合**结构
- 如果只有 key,没有伴随数据 value,可以使用 TreeSet 结构
- 如果既有 key,又有伴随数据 value,可以使用 TreeMap 结构
- 有无伴随数据,是 TreeSet 和 TreeMap 唯一的区别,底层的实际结构是一回事
- 有序表和哈希表的区别是,有序表把 key 按照顺序组织起来,而哈希表完全不组织
- 红黑树、AVL 树、size-balance-tree 和 跳表等都属于有序表,只是底层具体实现不同
- 放入有序表中的数据,如果是基础类型,内部按值传递,内存占用就是数据的大小
- 放入有序表中的数据,如果不是基础类型,必须提供比较器,内部按引用传递,内存占用是数据内存地址的大小
- 不管是什么底层具体实现,只要是有序表,都有固定的基本功能和固定的时间复杂度。
有序表的固定操作
以下所有操作的时间复杂度都是:O( logN ),N 为有序表含有的记录数
- put(key , value) :将一个(key,value)记录加入到表中,或者将 key 的记录更新成 value
- V get( key ):根据给定的 key,查询 value 并返回。
- remove( key ):移除 key 的记录
- containsKey( key ):询问是否有关于 key 的记录
- K firstKey():返回所有键值的排序结果中,最左(最小)的那个
- K lastKey():返回所有键值的排序结果中,最右(最大)的那个
- K floorKey( key ):如果表中存入过 key,返回 key,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,key 的前一个
- K ceilingKey( key ):如果表中存入过 key,返回 key,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,key 的后一个
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
treeMap.put(7, "我是7");
treeMap.put(5, "我是5");
treeMap.put(4, "我是4");
treeMap.put(3, "我是3");
treeMap.put(9, "我是9");
treeMap.put(2, "我是2");
System.out.println(treeMap.containsKey(5));
System.out.println(treeMap.get(5));
System.out.println(treeMap.firstKey() + ",我最小");
System.out.println(treeMap.lastKey() + ",我最大");
System.out.println(treeMap.floorKey(8) + ",在表中所有 <= 8 的数中,我离 8 最近");
System.out.println(treeMap.ceilingKey(8) + ",在表中所有 >= 8 的数中,我离 8 最近");
System.out.println(treeMap.floorKey(7) + ",在表中所有 <= 7 的数中,我离 7 最近");
System.out.println(treeMap.ceilingKey(7) + ",在表中所有 >= 7 的数中,我离 7 最近");
treeMap.remove(5);
System.out.println(treeMap.get(5) + ",删除就没有了哦");
}
常见的有序表
如果使用数组实现:put 和 remove 时需要移动数据。
如果使用链表实现:查询类都不满足 O(log N)
如果使用 HashMap 实现:HashMap 中是无序的,所以 firstKey,lastKey,floorKey,ceilingKey 操作不能满足时间复杂度:O(log N)
-
Binary Search Tree
-
SB(Size Blanced Tree)
-
AVL 树
-
红黑树
-
-
跳表
Binary Search Tree
二叉搜索树:支持快速查找,插入,删除一个数据。(log N)
定义:
- 根节点 > 左节点
- 根节点 < 右节点
性质:BST 中序遍历:结果是升序。
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
Find
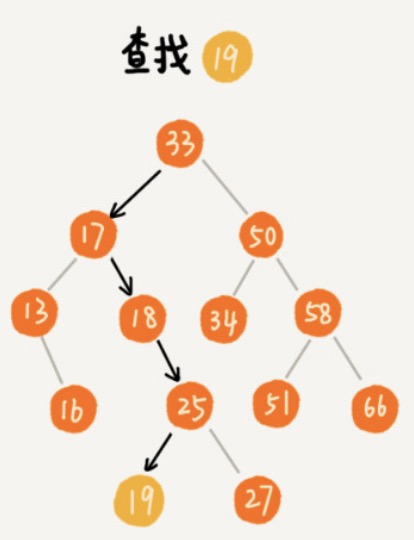
def find(self, data):
p = self.root
while p:
if data < p.data:
p = p.left
elif data > p.data:
p = p.right
else:
return p
与二分查有异曲同工之妙。
插入
新插入的数据一般都是在叶子节点上。
查找插入位置。

def insert(self, data):
if not self.root:
self.root = Node(data)
return
# 查找插入位置:节点 51
temp = self.root
while temp:
p = temp
temp = temp.left if data < temp.data else temp.right
if data < p.data:
p.left = Node(data)
else:
p.right = Node(data)
删除
真删除
删除操作分为三种情况:
- 要删除的节点没有子节点,将其父指向它的指针设为 null。
- 要删除的节点只有一个子节点,将其父节点指向它的指针,指向其子节点即可。
- 要删除的节点有两个子节点,找到这个节点右子树中最小的结点 min,将最小节点的值赋给要删除的节点,然后删除最小节点(或者找到这个节点左子树中最大的结点 max,用最大节点的值覆盖要删除节点的值,然后删除最大节点)。

代码:
def remove(self, data):
# p 指向要删除的节点
p = self.root
# p 的父节点
pp = Node
while p and p.data != data:
pp = p
if data > p.data:
p = p.right
else:
p = p.left
# 没有找到
if p is None: return
# 要删除的结点有两个子节点
if p.left and p.right:
# 查找右子树中,最小节点
min_p = p.right
min_pp = p
while min_p.left:
min_pp = min_p
min_p = min_p.left
# 将 min_p 的数据替换到 p 中
p.data = min_p.data
# 下边变成要删除 min_p
p = min_p
pp = min_pp
# 要删除节点是叶子节点或者仅有一个子节点
# child 是 p 的子节点
if p.left:
child = p.left
elif p.right:
child = p.right
else:
child = None
# 要删除的节点是根节点
if pp is None:
self.root = child
elif pp.left == p:
pp.left = child
else:
pp.right = child
软删除
删除时,将节点标记为“已删除”,这样删除和查找一样。
浪费空间,但是操作简单了很多。
查找最大节点
查找最大节点:一直右下去。
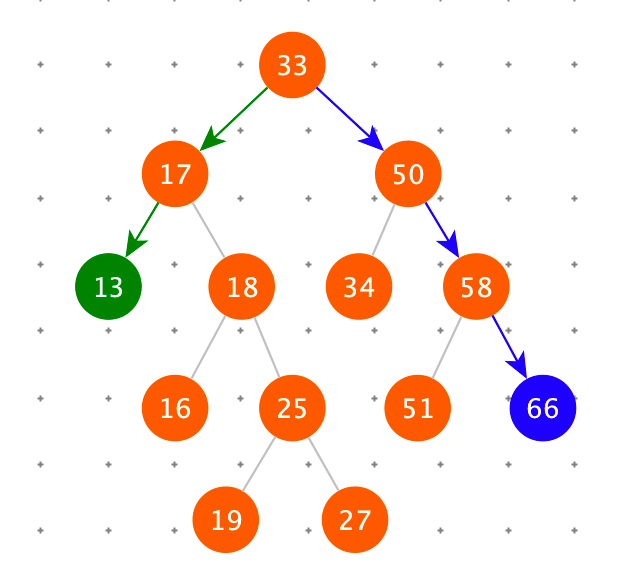
def last(self):
cur = self.root
while cur:
if cur.right:
cur = cur.right
else:
return cur.data
查找最小节点
查找最小节点:一直左下去
def first(self):
cur = self.root
while cur:
if cur.left:
cur = cur.left
else:
return cur.data
floor
如果表中存入过 key,返回 key,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,key 的前一个。

def floor(self, data):
res = None
cur = self.root
while cur:
if cur.data == data:
return cur
if cur.data > data:
cur = cur.left
else:
res = cur
cur = cur.right
return res
ceiling
如果表中存入过 key,返回 key,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,key 的后一个。
def ceiling(self, data):
res = None
cur = self.root
while cur:
if cur.data == data:
return cur
if cur.data > data:
res = cur
cur = cur.left
else:
cur = cur.right
return res
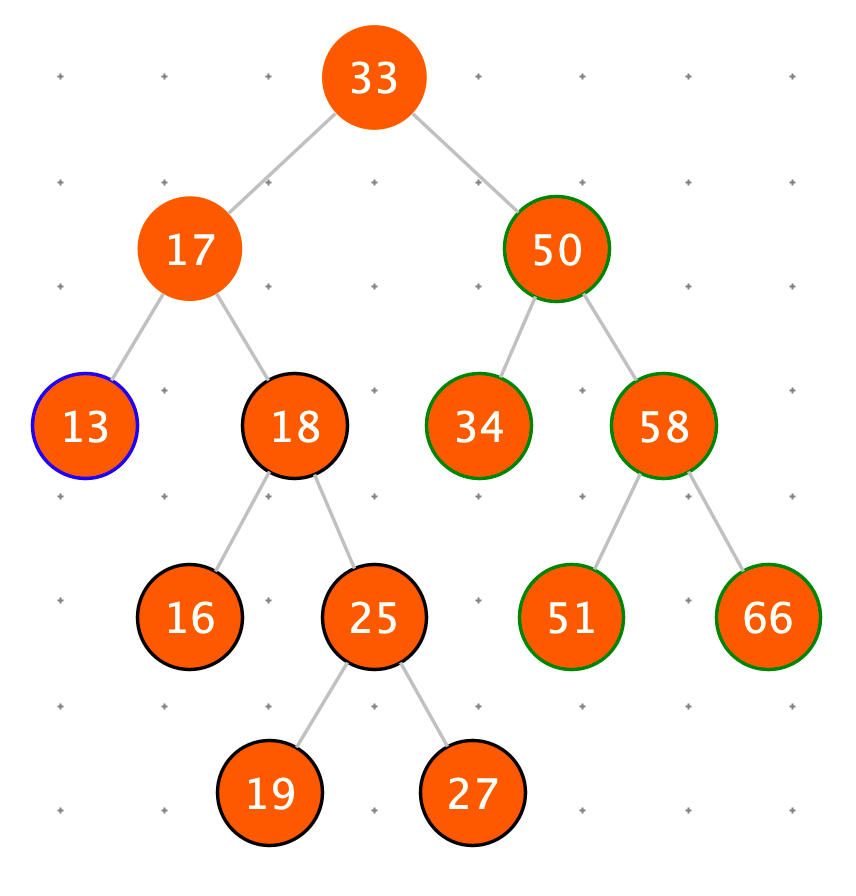
二叉查找树满足下边所有操作时间复杂度为 O ( log N )
- put(key , value) :将一个(key,value)记录加入到表中,或者将 key 的记录更新成 value
- V get( key ):根据给定的 key,查询 value 并返回。
- remove( key ):移除 key 的记录
- containsKey( key ):询问是否有关于 key 的记录
- K firstKey():返回所有键值的排序结果中,最左(最小)的那个
- K lastKey():返回所有键值的排序结果中,最右(最大)的那个
- K floorKey( key ):如果表中存入过 key,返回 key,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,key 的前一个
- K ceilingKey( key ):如果表中存入过 key,返回 key,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,key 的后一个
二叉查找树的问题
-
根节点左右子树极度不平衡,将退化为链表。这样查找的时间复杂度就变为:O(n).
最理想的情况:完全二叉树(或者满二叉树):查找的时间复杂度:$O(log_2{n})$
如何构建一棵不管怎么删除,插入数据,都是保持任意节点的左右子树都比较平衡的二叉查找树?
-
SB(Size Blanced Tree)
-
AVL 树
-
红黑树
这三棵树是在二叉搜索树基础上,解决了二叉搜索树的平衡性问题。
Size Balanced Tree
平衡性的定义:
- 每棵子树的大小(节点个数),不小于其兄弟的子树大小。既每棵叔叔树的大小,不小于其任何侄子树的大小。
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, value):
self.key = key
self.value = value
self.size = 1
self.left = None
self.right = None
平衡性解决方案
左旋
触发条件:cur = 节点 4,cur.right.right.size > cur.left.size。出现右边子树节点数太多。通过左旋,将 cur.right 的结点替换 cur 节点。

具体过程如下图
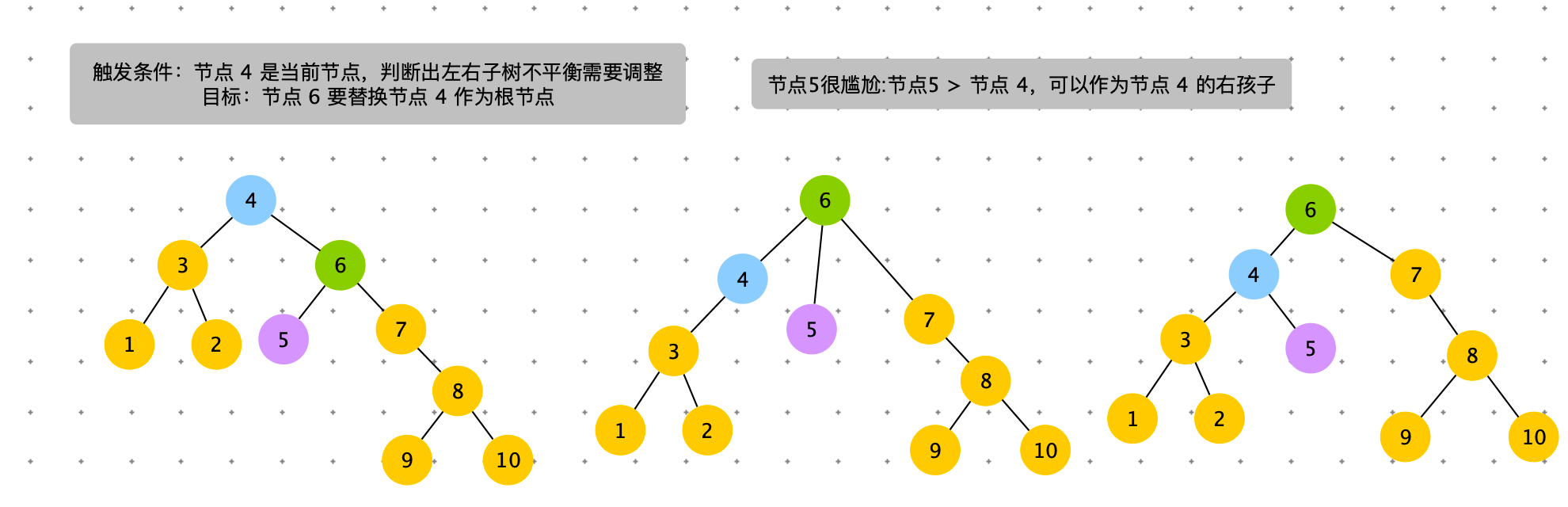
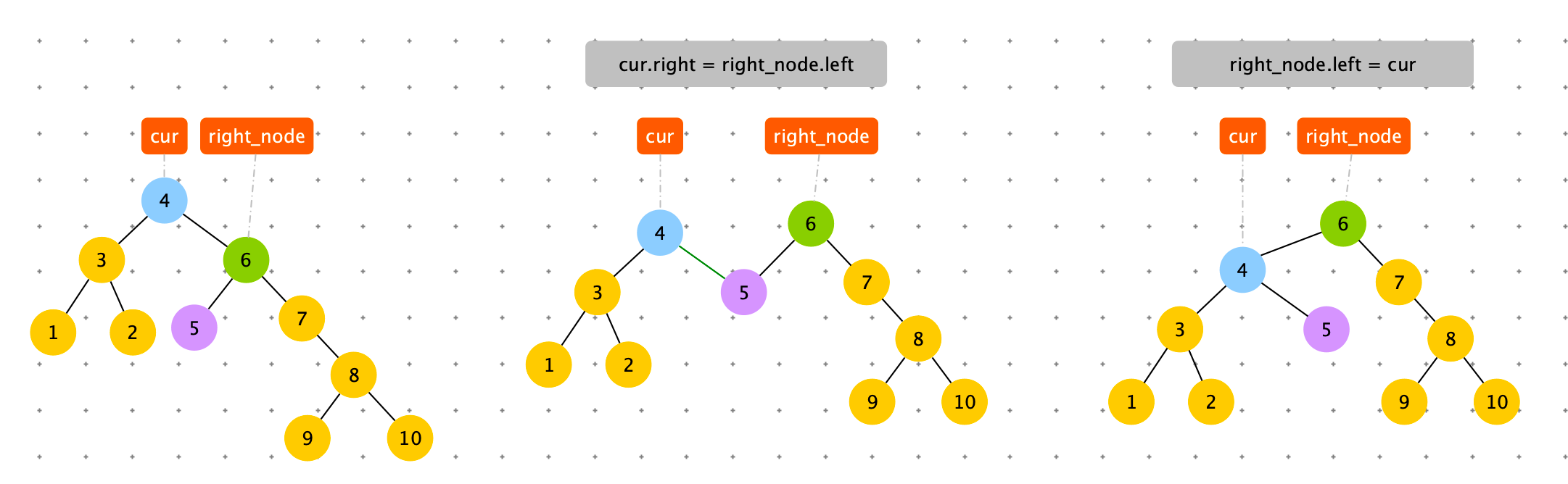
# 左旋
def left_rotate(self, cur: Node):
right_node = cur.right
cur.right = right_node.left
right_node.left = cur
# 此时 right_node 成为父节点
right_node.size = cur.size
cur.size = (cur.left.size if cur.left else 0) + (cur.right.size if cur.right else 0) + 1
return right_node
# 左旋触发时机
if right_right_size > left_size: # 左旋
cur = self.left_rotate(cur)
cur.left = self.maintain(cur.left)
cur = self.maintain(cur)
右旋
触发条件:cur = 节点 4,cur.left.left.size > cur.right.size。出现左边子树节点数太多。通过右旋,将 cur.left 的结点替换 cur 节点。
具体过程如下图

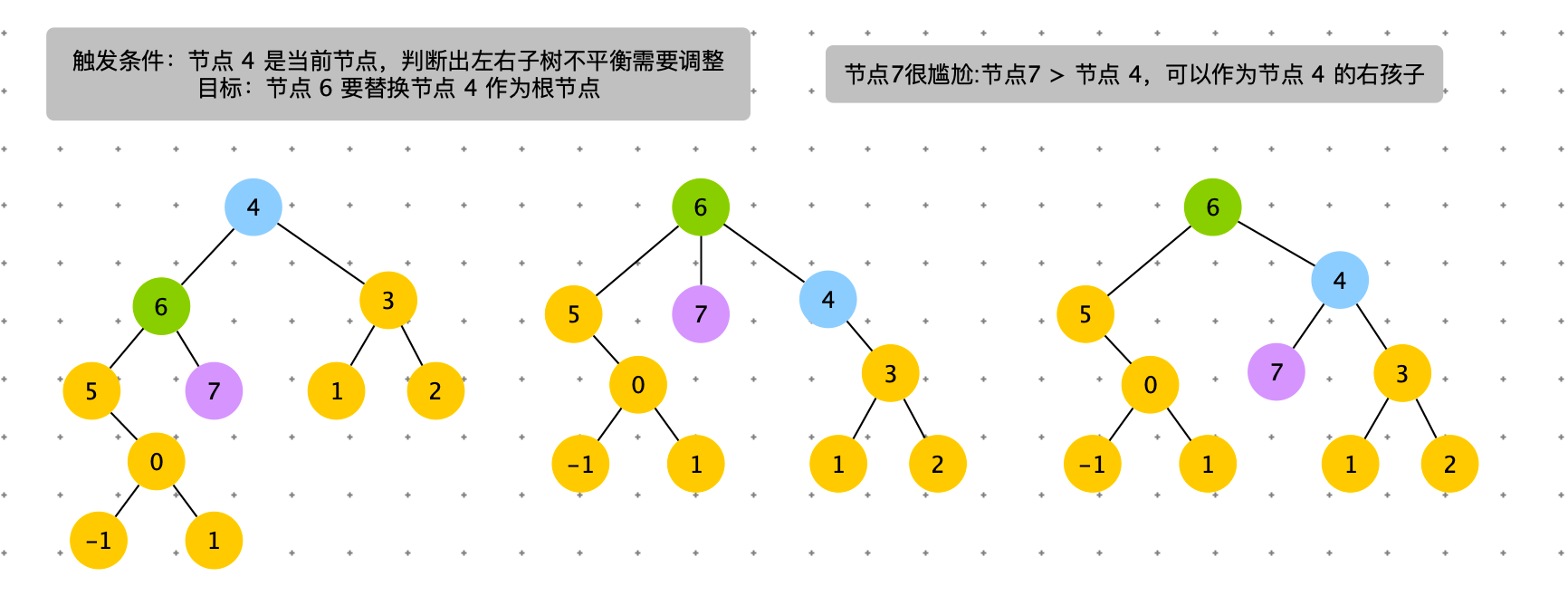

# 右旋
def right_rotate(self, cur: Node):
left_node = cur.left
cur.left = left_node.right
left_node.right = cur
# 此时 left_node 成为父节点
left_node.size = cur.size
cur.size = (cur.left.size if cur.left else 0) + (cur.right.size if cur.right else 0) + 1
return left_node
# 右旋触发时机
if left_left_size > right_size:
cur = self.right_rotate(cur)
cur.right = self.maintain(cur.right)
cur = self.maintain(cur)
左旋 + 右旋
触发条件:cur = 节点 4,cur.left.right.size > cur.right.size。出现左边子树节点数太多。通过右旋,将 cur.left 的结点替换 cur 节点。
具体过程如下图
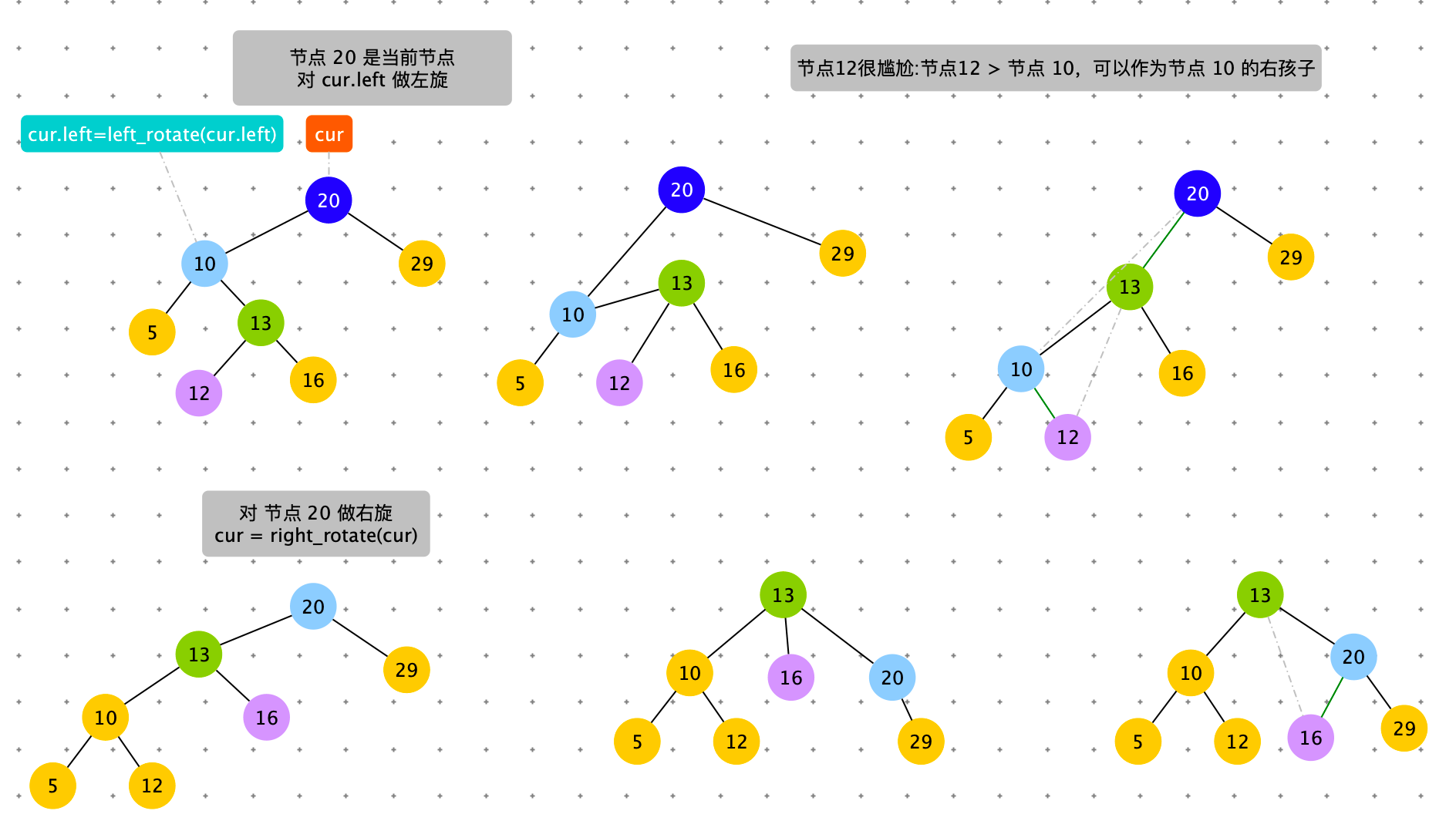
# 左旋,右旋:触发时机
if left_right_size > right_size: # 左旋,右旋
cur.left = self.left_rotate(cur.left)
cur = self.right_rotate(cur)
# 检查cur.left 是否平衡
cur.left = self.maintain(cur.left)
# 检查cur.right 是否平衡
cur.right = self.maintain(cur.right)
cur = self.maintain(cur)
右旋 + 左旋
触发条件:cur = 节点 4,cur.right.left.size > cur.left.size。出现左边子树节点数太多。通过右旋,将 cur.left 的结点替换 cur 节点。
具体过程如下图
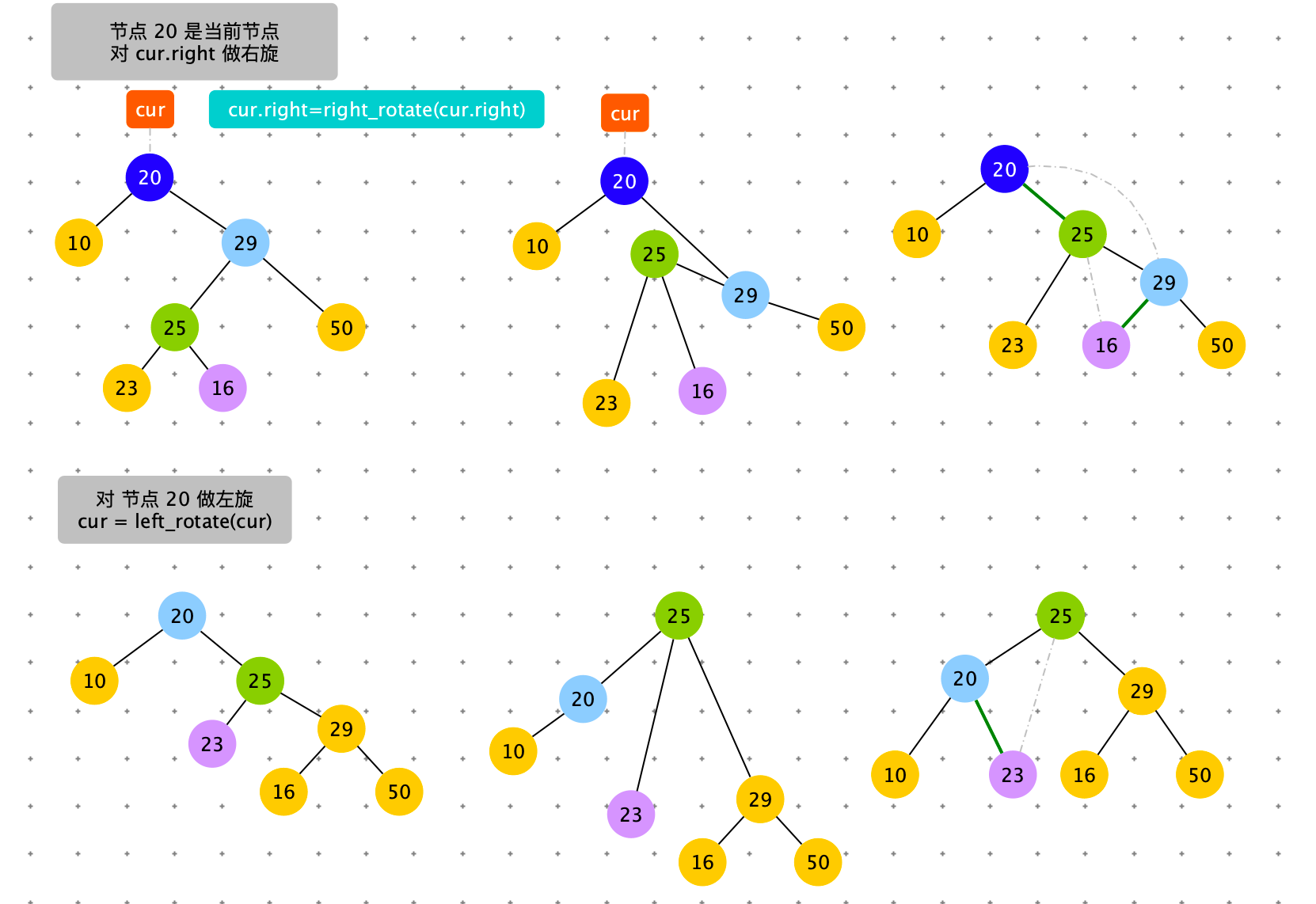
# 右旋,左旋:触发时机
if right_left_size > left_size: # 右旋,左旋
cur.right = self.right_rotate(cur.right)
cur = self.left_rotate(cur)
cur.left = self.maintain(cur.left)
cur.right = self.maintain(cur.right)
cur = self.maintain(cur)
旋转触发的时机
新增数据,删除数据后,调用一下 maintain
def maintain(self, cur: Node):
if not cur: return
left_size = cur.left.size if cur.left else 0
left_left_size = cur.left.left.size if cur.left and cur.left.left else 0
left_right_size = cur.left.right.size if cur.left and cur.left.right else 0
right_size = cur.right.size if cur.right else 0
right_right_size = cur.right.right.size if cur.right and cur.right.right else 0
right_left_size = cur.right.left.size if cur.right and cur.right.left else 0
# 右旋
if left_left_size > right_size:
cur = self.right_rotate(cur)
cur.right = self.maintain(cur.right)
cur = self.maintain(cur)
elif left_right_size > right_size: # 左旋,右旋
cur.left = self.left_rotate(cur.left)
cur = self.right_rotate(cur)
cur.left = self.maintain(cur.left)
cur.right = self.maintain(cur.right)
cur = self.maintain(cur)
elif right_right_size > left_size: # 左旋
cur = self.left_rotate(cur)
cur.left = self.maintain(cur.left)
cur = self.maintain(cur)
elif right_left_size > left_size: # 右旋,左旋
cur.right = self.right_rotate(cur.right)
cur = self.left_rotate(cur)
cur.left = self.maintain(cur.left)
cur.right = self.maintain(cur.right)
cur = self.maintain(cur)
return cur
AVL 树
AVL 树是一种平衡二叉树,得名于其发明者的名字( Adelson-Velskii 以及 Landis)。
平衡性定义:左右子树的高度差小于等于 1。
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, value):
self.key = key
self.value = value
self.height = 1
self.left = None
self.right = None
红黑树
红黑树的定义:
- 任何一个节点都有颜色,黑色或者红色
- 根节点是黑色的
- 父子节点之间不能出现两个连续的红节点
- 任何一个节点向下遍历到其子孙的叶子节点,锁经过的黑色节点个数必须相等。
- 空节点被认为是黑色节点
SkipLists
- 跳表是一个随机化的搜索数据结构

- put(key , value) :将一个(key,value)记录加入到表中,或者将 key 的记录更新成 value
- V get( key ):根据给定的 key,查询 value 并返回。
- remove( key ):移除 key 的记录
- containsKey( key ):询问是否有关于 key 的记录
- K firstKey():返回所有键值的排序结果中,最左(最小)的那个
- K lastKey():返回所有键值的排序结果中,最右(最大)的那个
- K floorKey( key ):如果表中存入过 key,返回 key,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,key 的前一个
- K ceilingKey( key ):如果表中存入过 key,返回 key,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,key 的后一个
跳表的 NB 之处:
- 思想先进:跳表不再使用硬规则来数据的平衡性,而是使用概率保证。
- 由于使用概率随机生成数据层,与用户输入的数据无关。
跳表时间复杂度评估
第 0 层:N 个节点(每个节点必在第 0 层)
第 1 层:$\frac{N}{2}$ 个节点
第 2 层:$\frac{N}{4}$ 个节点
第 3 层:$\frac{N}{8}$ 个节点
…
第 k 层:$\frac{N}{2^k}$ 个节点
类似满二叉树
查找数据
查找 50 。从 head 的最上层开始查找,如果节点小于 50 就 next,否则就下降一层查找。
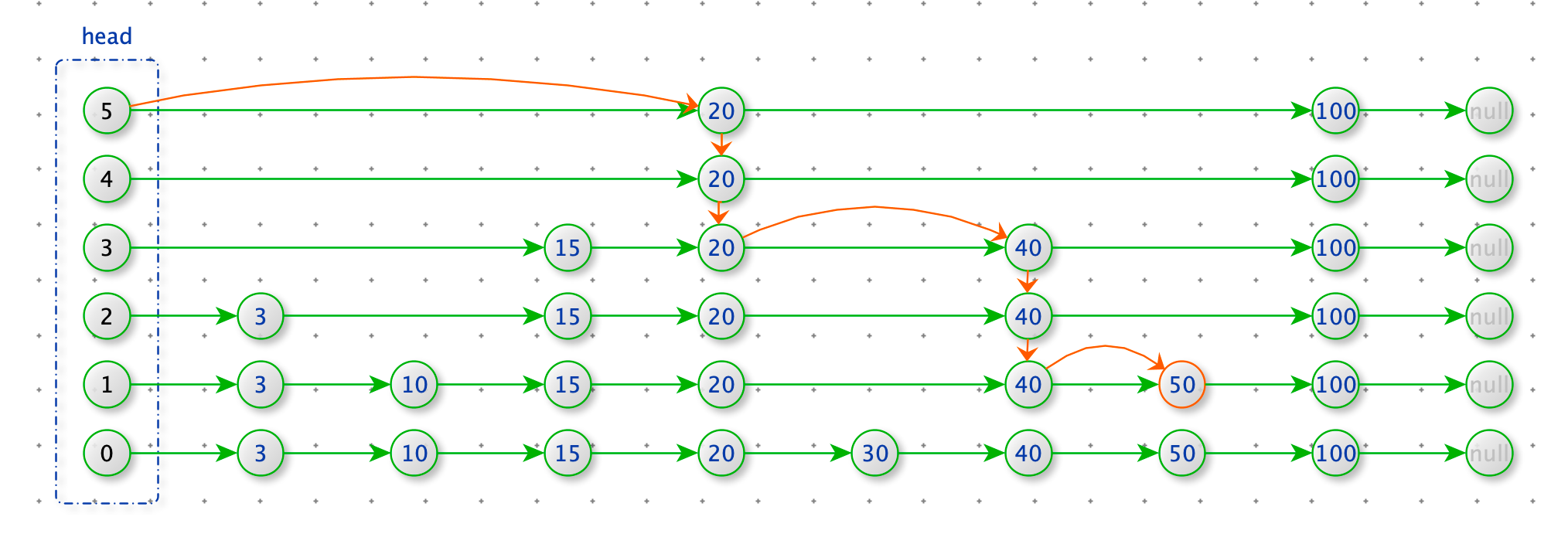
def find(self, value):
p = self.head
for i in range(len(self.head.next_nodes) - 1, -1, -1):
while p.next_nodes[i] and p.next_nodes[i].value < value:
p = p.next_nodes[i]
if p.next_nodes[0] and p.next_nodes[0].value == value:
return p.next_nodes[0].value
添加数据
新增数据 70,随机出 70 需要的层数(以等概率出现 0 和 1 ,当出现 1 时层数+1,当出现 0 时结束。但是要保证至少有一层)
如下图:70 随机出了 7 层 大于 head 的层数,所以 head 需要扩展层数到 7 层。
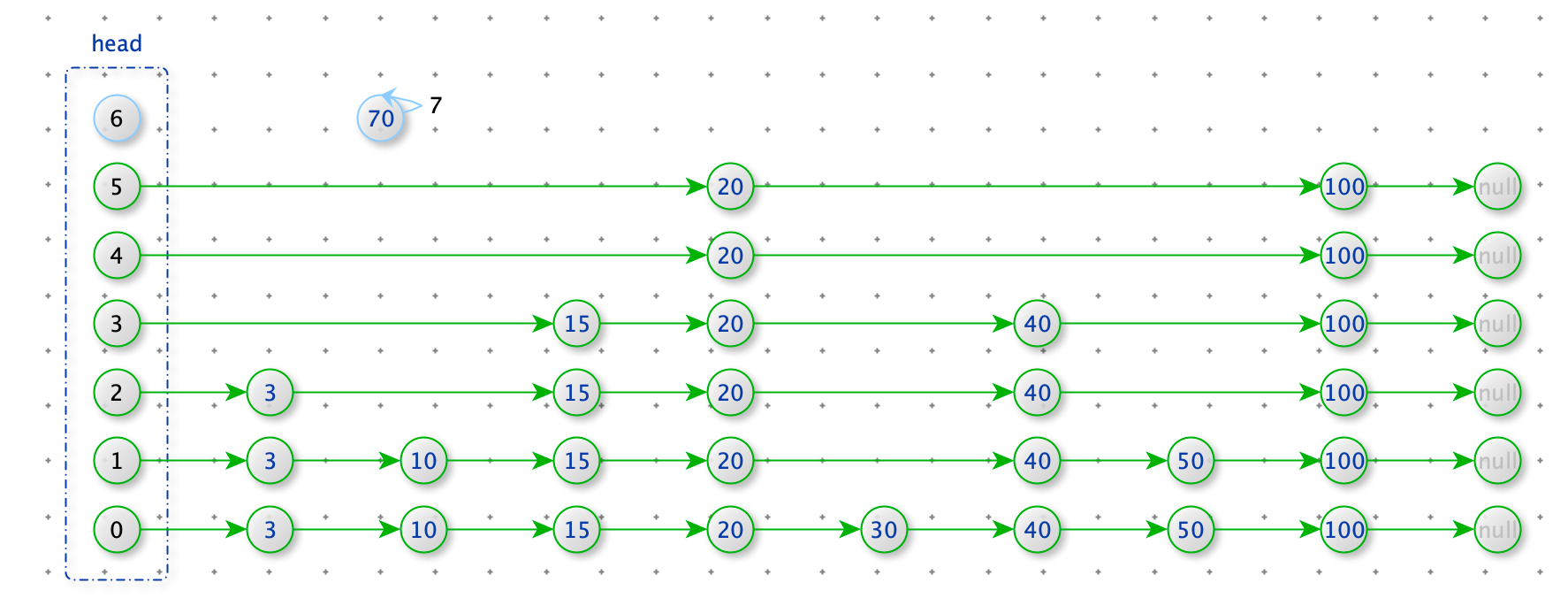
def expand_head(self, level):
n = len(self.head.next_nodes)
if level < n:
return
for _ in range(level - n):
self.head.next_nodes.append(None)
def get_random_level(self):
res = 0
while int(random.random() * 2) != 0:
res += 1
return min(max(res,1), math.log (self.node_count + 1))
查找插入为位置:从 head 的最上层开始查找,寻找每一层小于 70 的最后的节点。

插入节点:根据 70 节点的层数,从上向下加入到每一层,加入位置就是上边查找的位置。

def insert(self, value):
self.insert_level(value, self.get_random_level())
def insert_level(self, value, level):
self.expand_head(level)
new_node = Node(value, level)
update_arr = [self.head] * len(self.head.next_nodes)
p = self.head
n = len(self.head.next_nodes)
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
while p.next_nodes[i] and p.next_nodes[i].value < value:
p = p.next_nodes[i]
update_arr[i] = p
# 加入 new_node
for i in range(level):
new_node.next_nodes[i] = update_arr[i].next_nodes[i]
update_arr[i].next_nodes[i] = new_node
删除数据
删除节点 15
查找删除为位置:从 head 的最上层开始查找,寻找每一层小于 15 的最后的节点。
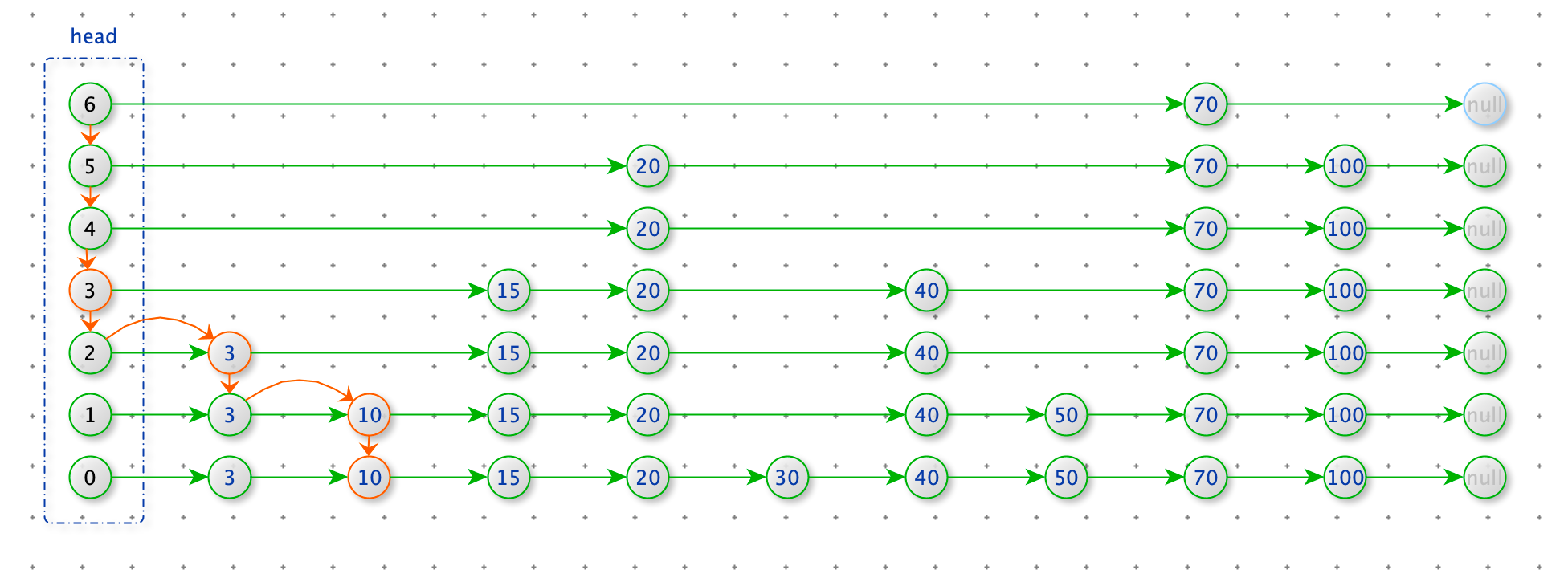
删除节点:如果上一步的节点的 node.next_node.value = 15,那么 node.next_node = node.next_node.next_node

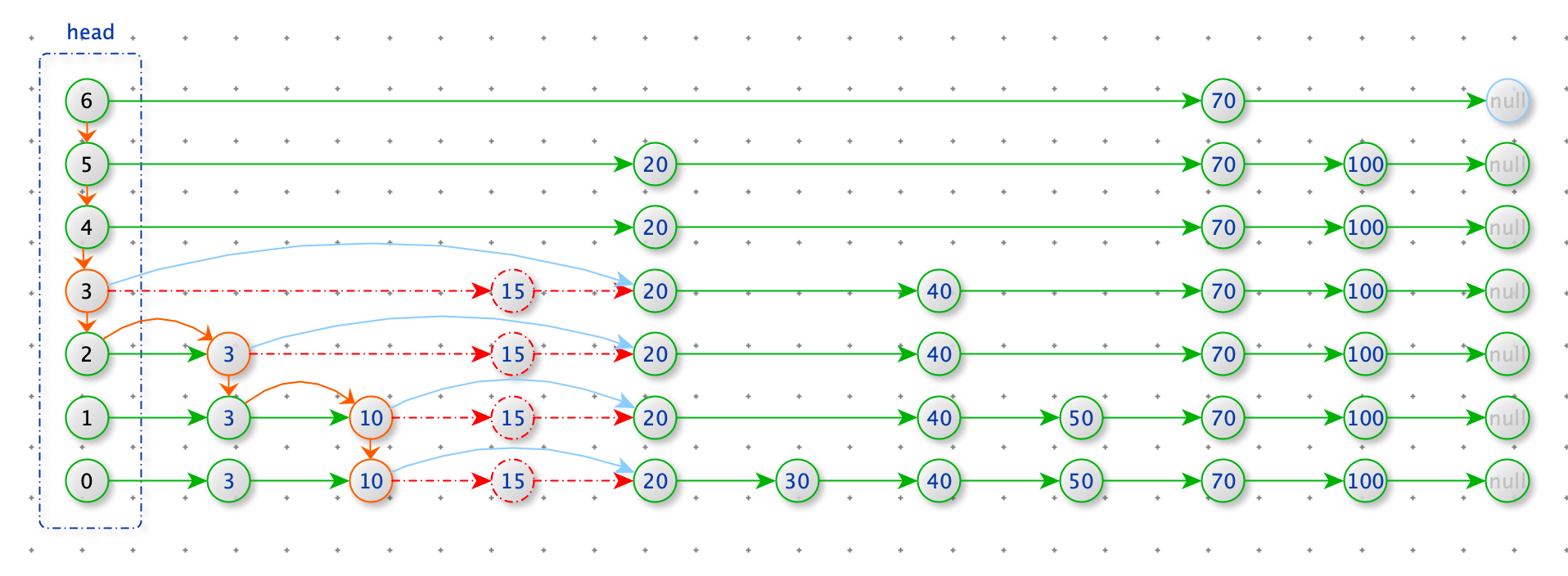
def delete(self, value):
n = len(self.head.next_nodes)
update_arr = [None] * n
p = self.head
# 查找需要更新结点
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
while p.next_nodes[i] and p.next_nodes[i].value < value:
p = p.next_nodes[i]
update_arr[i] = p
# 如果没有删除节点,直接返回
if p.next_nodes and p.next_nodes[0].value != value: return
# 删除节点
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
if update_arr[i].next_nodes[i] and update_arr[i].next_nodes[i].value == value:
update_arr[i].next_nodes[i] = update_arr[i].next_nodes[i].next_nodes[i]
floor

floor(60); node = 50
# 如果表中存入过 value,返回 value,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,value 的前一个
def floor(self, value):
node = self.find(value)
if node.next_nodes[0] and node.next_nodes[0].value == value:
return value
return node.value
ceiling
floor(60);node = 50;node.next_nodes[0].value = 70
# 如果表中存入过 value,返回 value,否则返回所有键值的排序结果中,value 的后一个
def ceiling(self, value):
node = self.find(value)
if node.next_nodes[0] and node.next_nodes[0].value == value:
return value
if node.next_nodes[0]:
return node.next_nodes[0].value
业务中经常需要存储一些伴随数据(业务数据)
import random
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, value, max_level):
# 伴随数据
self.value = value
self.key = key
self.next_nodes = [None] * max_level
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.key < other
def __eq__(self, other):
return self.key == other
def __ge__(self, other):
return self.key > other
class SkipListMap:
def __init__(self):
self.head = Node(-1, -1, 1)
def insert(self, key, value):
self.insert_level(key, value, self.get_random_level())
def insert_level(self, key, value, level):
self.expand_head(level)
new_node = Node(key, value, level)
update_arr = [self.head] * len(self.head.next_nodes)
p = self.head
n = len(self.head.next_nodes)
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
while p.next_nodes[i] and p.next_nodes[i].key < key:
p = p.next_nodes[i]
update_arr[i] = p
# 加入 new_node
for i in range(level):
new_node.next_nodes[i] = update_arr[i].next_nodes[i]
update_arr[i].next_nodes[i] = new_node
def delete(self, key):
n = len(self.head.next_nodes)
update_arr = [None] * n
p = self.head
# 查找需要更新结点
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
while p.next_nodes[i] and p.next_nodes[i].key < key:
p = p.next_nodes[i]
update_arr[i] = p
# 删除节点
if p.next_nodes and p.next_nodes[0].value != key: return
# 删除节点
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
if update_arr[i].next_nodes[i] and update_arr[i].next_nodes[i].value == key:
update_arr[i].next_nodes[i] = update_arr[i].next_nodes[i].next_nodes[i]
def expand_head(self, level):
n = len(self.head.next_nodes)
if level < n:
return
for _ in range(level - n):
self.head.next_nodes.append(None)
def get_random_level(self):
res = 1
while int(random.random() * 2) != 0:
res += 1
return res
def find(self, key):
p = self.head
for i in range(len(self.head.next_nodes) - 1, -1, -1):
while p.next_nodes[i] and p.next_nodes[i].key < key:
p = p.next_nodes[i]
return p
def __contains__(self, item):
node = self.find(item)
return node.next_nodes[0] and node.next_nodes[0].key == item
def first(self):
return self.head.next_nodes[0].key
def last(self):
p = self.head
n = len(self.head.next_nodes)
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
while p.next_nodes[i]:
p = p.next_nodes[i]
return p.key
def floor(self, key):
node = self.find(key)
if node.next_nodes[0] and node.next_nodes[0].value == key:
return key
return node.key
def ceiling(self, key):
node = self.find(key)
if node.next_nodes[0] and node.next_nodes[0].value == key:
return key
if node.next_nodes[0]:
return node.next_nodes[0].key
skipList = SkipListMap()
skipList.insert_level(3, None, 3)
skipList.insert_level(10, None, 2)
skipList.insert_level(15, None, 4)
skipList.insert_level(20, None, 6)
skipList.insert_level(30, None, 1)
skipList.insert_level(40, None, 4)
skipList.insert_level(50, None, 5)
skipList.insert_level(70, None, 2)
skipList.insert_level(100, None, 6)
print(40 in skipList)
print(60 in skipList)
print(skipList.first())
print(skipList.last())
print("-" * 100)
print(skipList.ceiling(50))
print(skipList.ceiling(60))
print(skipList.floor(50))
print(skipList.floor(60))
应用
为了找到自己满意的工作,牛牛收集了每种工作的难度和报酬。牛牛选工作的标准是在难度不超过自身能力值的情况下,牛牛选择报酬最高的工作,在牛牛选定了自己的工作以后,牛牛的小伙伴们来找牛牛帮忙选工作,牛牛依然使用自己的标准来帮助小伙伴。牛牛的小伙伴太多了,于是他只好把这个任务交给了你。
输入参数:
- Job_arr:表示所有的工作。
- Int_arr:表示所有小伙伴的能力值。
返回数据:int_arr 表示每个小伙伴按照牛牛的标准选工作后所能获得的报酬。
步骤:
- hard 升序,money 降序,对 job_arr 排序
- 将 hard 相同,money 最大的 job 加入有序表(TreeMap),如果当前 money 小于之前的 job 也要排除(例如任务3的money 小于任务 2)。
- 遍历 int_arr 数据,从有序表 treeMap floorEntry (获取能力能达到最大Job,将对应money 写入 result )

public static class Job {
// 工作报酬
public int money;
// 工作难度
public int hard;
public Job(int hard, int money) {
this.money = money;
this.hard = hard;
}
}
public static class JobComparator implements Comparator<Job> {
@Override
public int compare(Job o1, Job o2) {
return o1.hard != o2.hard ? o1.hard - o2.hard : o2.money - o1.money;
}
}
public static int[] getMoneys(Job[] jobs, int[] ability) {
Arrays.sort(jobs, new JobComparator());
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
int money = 0;
for (Job job : jobs) {
if (treeMap.containsKey(job.hard) || job.money <= money) {
continue;
}
money = Math.max(money, job.money);
treeMap.put(job.hard, job.money);
}
int[] res = new int[ability.length];
for (int i = 0; i < ability.length; i++) {
int item = ability[i];
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry = treeMap.floorEntry(item);
if (entry == null) {
continue;
}
res[i] = entry.getValue();
}
return res;
}
public static int[] getMoneys2(Job[] jobs, int[] ability) {
Arrays.sort(jobs, new JobComparator());
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
// 由于已经排序,hard 相同并且 money 大的一定排在第一名,只需要将第一名插入 treeMap 中
// 需要 pre 记录每组的第一个 job,即可区分不同的组
// 时间复杂度从 O(N log N) 下降到 O(N)
Job pre = jobs[0];
for (int i = 1; i < jobs.length; i++) {
if (jobs[i].hard != pre.hard && jobs[i].money > pre.money) {
treeMap.put(jobs[i].hard, jobs[i].money);
pre = jobs[i];
}
}
int[] res = new int[ability.length];
for (int i = 0; i < ability.length; i++) {
int item = ability[i];
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry = treeMap.floorEntry(item);
if (entry == null) {
continue;
}
res[i] = entry.getValue();
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Job[] jobs = new Job[8];
jobs[0] = new Job(3, 5);
jobs[1] = new Job(2, 7);
jobs[2] = new Job(9, 100);
jobs[3] = new Job(1, 4);
jobs[4] = new Job(2, 6);
jobs[5] = new Job(3, 3);
jobs[6] = new Job(1, 1);
jobs[7] = new Job(2, 8);
int[] ability = new int[]{0, 2, 8, 9, 10};
for (int item : getMoneys(jobs, ability)) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
